Histopathological evaluation of staging, grading and prognostic factors of renal cell carcinoma
Abstract
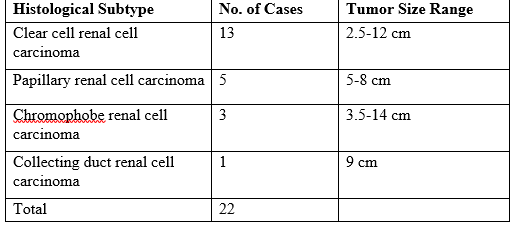
Introduction: Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is a malignancy with an adverse prognosis for the majority of the patients. Renal cell carcinoma accounts for 80% to 85% of malignant kidney tumors. Despite that an increasing number of patients incidentally are diagnosed, still around 25–30% of patients with new diagnosed disease already have metastatic disease. Of the remaining patients with nonmetastatic disease, about 30–40% will progress with distant metastases or local recurrent RCC. Objective: To assess the prognosis of age, sex, race, tumor size, pathological staging, grading and prognostic factors of Renal Cell Carcinoma. Material and Methods: In the retrospective study was done in Department of Urology, Sir Salimullah Medical College, Mitford, Dhaka, Bangladesh from June 2021 to July 2022. A total number of 101 nephrectomy specimens were analyzed and 22 diagnosed cases of renal cell carcinoma were included in the study. The age and sex distribution of renal cell carcinomas diagnosed were study. Histopathological evaluation of renal cell carcinomas was carried out correlating with old records, histopathology slides, special stains and immunohistochemistry. Results: Total 101 nephrectomy specimens were analyzed and 22 diagnosed cases of renal cell carcinoma were included in the study. Maximum numbers of cases were seen in 40-49 years’ age group (31.8%) and also in 60-69 years’ age group (31.8%). Histological subtypes of renal cell carcinoma diagnosed were Clear cell type, papillary type, Chromophobe type and Collecting duct type. Maximum numbers of cases diagnosed were of Clear cell type renal cell carcinoma (59.09%). Least common subtype diagnosed was Collecting duct type renal cell carcinoma (4.5%). Least common subtype diagnosed was Collecting duct renal cell carcinoma (4.5%). Tumor size was >4cm in maximum number of cases i.e. 20 (72.8%). Most of the subtypes of renal cell carcinoma had Fuhrman nuclear grades 2 and 3. Out of 22 cases of renal cell carcinoma, sarcomatoid differentiation was observed histologically in 3 cases (13.6%) within the tumor tissue. 2 cases of Clear cell type and 1 case of papillary type of renal cell carcinoma had sarcomatoid differentiation. Conclusion: In concluded, the underscores the importance of nuclear grading in predicting survival of renal cell carcinoma patients. There is strong correlation between grade, tumor size, and stage. Nuclear grading is important in predicting survival of patients with renal cell carcinoma. Nuclear grading is strongly related to both tumor size and stage. Nuclear grading and staging of the histological subtypes strongly influences the survival of patients, as thus proven in this study.
Downloads
References
Cohen HT, McGovern FJ. Renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2005; 353: 2477– 2490.
Pantuck AJ, Zisman A, Belldegrun AS. The changing natural history of renal cell carcinoma. J Urol. 2001; 166: 1611–1623.
Ficarra V, Righetti R, Pilloni S, et al. Prognostic factors in patients with renal cell carcinoma: retrospective analysis of 675 cases. Eur Urol 2002; 41(2): 190–8.
Lohse CM, Blute ML, Zincke H, Weaver AL, Cheville JC. Comparison of standardized and non-standardized nuclear grade of renal cell carcinoma to predict outcome among 2,042 patients. Am J Clin Pathol 2002; 118: 877-86.
Kovacs G, Akhtar M, Beckwith BJ, et al. The Heidelberg classification of renal cell tumors. J Pathol 1997; 183(2): 131-3.
Eble JN, Sauter G, Epstein JI, Sesterhenn IA, eds. World Health Organization classification of tumors: pathology and genetics of tumours of the urinary system and male genital organs. Lyons: IARC Press; 2004.
Lau WK, Cheville JC, Blute ML, Weaver AL, Zincke H. Prognostic features of pathologic stage T1 renal cell carcinoma after radical nephrectomy. Urology 2002; 59(4): 532–7.
Beck SD, Patel MI, Snyder ME, et al. Effect of papillary and chromophobe cell type on disease-free survival after nephrectomy for renal cell carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol 2004; 11(1): 71–7.
Gettman MT, Blute ML, Spotts B, Bryant SC, Zincke H. Pathologic staging of renal cell carcinoma: significance of tumor classification with the 1997 TNM staging system. Cancer 2001; 91: 354-61.
Ficarra V, Righetti R, Martignoni G, et al. Prognostic value of renal cell carcinoma nuclear grading: multivariate analysis of 333 cases. Urol Int 2001; 67: 130-4.
Fuhrman SA, Lasky LC, Limas C. Prognostic significance of morphologic parameters in renal cell carcinoma. Am J Surg Pathol 1982; 6: 655-63.
Lee CT, Katz J, Shi W, Thaler HT, Reuter VE and Russo P: Surgical management of renal tumors 4 cm. or less in a contemporary cohort. J Urol 2000; 163: 730.
Saranchuk JW, Touijer AK, Hakimian P, Snyder ME and Russo P: Partial nephrectomy for patients with a solitary kidney: the Memorial Sloan-Kettering experience. BJU Int 2004; 94: 323.
Thompson RH, Leibovich BC, Lohse CM, Zincke H and Blute ML: Complications of contemporary open nephron sparing surgery: a single institution experience. J Urol 2005; 174: 855.
10. Finley DS, Beck S, Box G, Chu W, Deane L, Vajgrt DJ et al: Percutaneous and laparoscopic cryoablation of small renal masses. J Urol 2008; 180: 492.
Frank I, Blute ML, Cheville JC, Lohse CM, Weaver AL and Zincke H: Solid renal tumors: an analysis of pathological features related to tumor size. J Urol 2003; 170: 2217.
Nathalie Rioux-Leclercq, Pierre I. Karakiewicz, Quoc-Dien Trinh, Vincenzo Ficarra, Luca Cindolo, Alexandre de la Taille et al. American Cancer Society 2007; 109: 868-874.
Tomas Gudbjartsson, Sverrir Hardarson, Vigdis Petursdottir, Asgeir Thoroddsen, Jonas Magnusson, Gudmundur V. Einarsson. Histological Subtyping and Nuclear Grading of Renal Cell Carcinoma and Their Implications for Survival: A Retrospective NationWide Study of 629 Patients. Eur Urol 2005; 48: 593-600.
Pierre I. Karakiewicz, Alberto Briganti, Felix K.-H. Chun, Quoc-Dien Trinh, Paul Perrotte, Vincenzo Ficarra et al. MultiInstitutional Validation of a New Renal Cancer–Specific Survival Nomogram. J Clinical Oncol 2007; 25: 1316-1322.
Ficarra V, Guille F, Schips L, et al. Proposal for revision of the TNM classification system for renal cell carcinoma. Cancer. 2005; 104: 2116-2123.
[16]. Gettman MT, Blute ML. Update on pathologic staging of renal cell carcinoma. Urology 2002; 60: 209-17.
Kovacs G, Akhtar M, Beckwith BJ, et al. The Heidelberg classification of renal cell tumors. J Pathol 1997; 183(2): 131-3.
Eble JN, Sauter G, Epstein JI, Sesterhenn IA, eds. World Health Organization classification of tumors: pathology and genetics of tumours of the urinary system and male genital organs. Lyons: IARC Press; 2004.
R. Houston Thompson, Jordon, Matthew, Satish. K. Tumor size is associated with malignant potential in renal cell carcinoma cases. Journal of Urology. 2009; 181: 2033-36.
De Peralta-Venturina M, Moch H, Amin M, et al. Sarcomatoid differentiation in renal cell carcinoma: a study of 101 cases. Am Surg Pathol 2001; 25: 275-84.