Empagliflozin, Linagliptin, and Metformin in a triple fixed-dose combination for individuals with type 2 diabetes
Abstract
As per the International Diabetes Federation (IDF), the percentage of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is increasing globally. Tight glycemic control is a crucial aspect of the management of T2DM due to the progressive nature of the disease. Evidence advises that aggressive glycemic control is beneficial not only for the short-term but also for the long-term well-being of patients. Due to the progressive nature of T2DM, first-line therapy often fails to provide effective glycemic control, necessitating the addition of add-on therapy. Hence, FDCs can play a crucial role in achieving glycemic targets effectively. Also, patients who are unable to tolerate metformin or who experience side effects of metformin monotherapy receive fixed-dose combinations (FDCs) of various other oral antidiabetic agents (OAD) including sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 (SGLT-2) inhibitors, dipeptidyl peptidase (DPP-4) inhibitors, thiazolidinediones (TZDs), sulfonylureas (SUs), glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) antagonist, and basal insulin. The addition of the third agent can also be considered to enhance treatment efficacy.
Downloads
References
Kalra S, Das AK, Priya G, Ghosh S, Mehrotra RN, Das S, et al. Fixed-dose combination in the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus: Expert opinion from an international panel. J Family Med Prim Care 2020; 9:5450-7.
Böhm AK, Schneider U, Aberle J, Stargardt T. Regimen simplification and medication adherence: Fixed-dose versus loose-dose combination therapy for type 2 diabetes. PLoS One. 2021;16(5):e0250993. Published 2021 May 4. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0250993
Goldman JD. Combination of Empagliflozin and Metformin Therapy: A Consideration of its Place in Type 2 Diabetes Therapy. Clinical Medicine Insights: Endocrinology and Diabetes. January 2018. doi:10.1177/1179551418786258
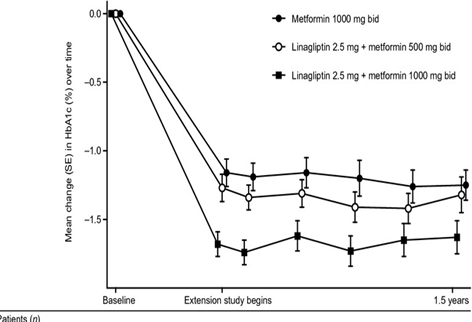
Haak T, Meinicke T, Jones R, Weber S, von Eynatten M, Woerle HJ. The initial combination of linagliptin and metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes: efficacy and safety in a randomized, double-blind 1-year extension study. Int J Clin Pract. 2013;67(12):1283-1293. doi:10.1111/ijcp.12308
Haak. Combination of linagliptin and Metformin for the Treatment of Patients with type 2 diabetes. Clinical Medicine Insights: Endocrinology and Diabetes 2015:8 1–6 doi:10.4137/CMED.S10360.
Lingvay, I., Beetz, N., Sennewald, R., Schuler-Metz, A., Bertulis, J., Loley, C.,Terada, D. (2020). The triple fixed-dose combination of empagliflozin, linagliptin, and metformin for patients with type 2 diabetes. Postgraduate Medicine, 1–9. doi:10.1080/00325481.2020.1750228
Søfteland E, Meier JJ, Vangen B, Toorawa R, Maldonado-Lutomirsky M, Broedl UC. Empagliflozin as Add-on Therapy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Inadequately Controlled With Linagliptin and Metformin: A 24-Week Randomized, Double-Blind, Parallel-Group Trial. Diabetes Care. 2017 Feb;40(2):201-209. doi: 10.2337/dc16-1347. Epub 2016 Dec 2. PMID: 27913576.