Clinico-Demographic and Radiological Profile of Bronchiolitis Patients in a Tertiary Care Hospital in Bangladesh
Abstract
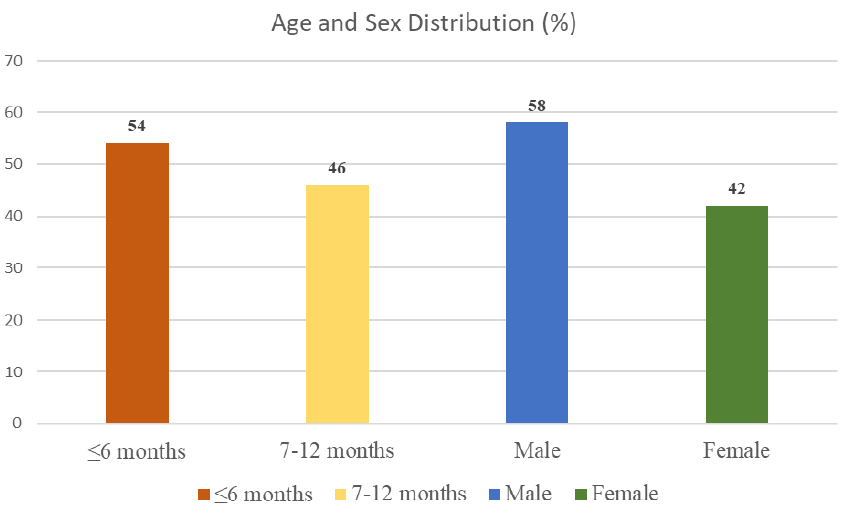
Background: Bronchiolitis is the most common cause of hospitalization in infants below 2 years of age. It usually presents with breathing difficulty, cough, fever and runny nose. The treatment of bronchiolitis mainly supportive. Objectives: The aim of this study was to find out the clinico-demographic and radiological characteristics of bronchiolitis for its proper diagnosis and management. Methods: This is a cross-sectional observational study was done in the Department of Pediatrics, Bangladesh Shishu Hospital and Institute from July 2019 to June 2021. A total 100 patients between ages of 2-months to 1-year admitted with the diagnosis of bronchiolitis, were included in this study. Data were collected in the form of age, gender, clinical features, laboratory and radiological findings Results: most of the cases are less than 6 months and the majority patients were males (58%) and females were (42%). Cough, fast breathing and wheezing were present in most of the children. all patient had difficulty in breathing and chest indrawing. Cough was a presenting feature of 96% cases, fast breathing was in 89% cases. Wheezing was in (82%) cases. Predominant radiological findings are hyperinflation and hypertranslucency. Hypertranslucency was present in 97% cases whereas hyperinflation was present in 93% cases. Conclusion: We concluded that bronchiolitis patients present with typical clinical and radiological features which can help for its diagnosis and management.
Downloads
References
Verma N, Lodha R, Kabra SK. Recent advances in management of bronchiolitis. Indian pediatrics. 2013 Oct; 50:939-49.
Koley G, Koley KC. Comparison of salbutamol to adrenaline nebulization in acute severe bronchiolitis: An original research paper. International Journal of Scientific Study. 2017;5(2):202-5.
Ralston SL, Lieberthal AS, Meissner HC, Alverson BK, Baley JE, Gadomski AM, Johnson DW, Light MJ, Maraqa NF, Mendonca EA, Phelan KJ. Clinical practice guideline: the diagnosis, management, and prevention of bronchiolitis. Pediatrics. 2014 Nov 1;134(5): e1474-502.
Modaressi MR, Asadian A, Faghihinia J, Arashpour M, Mousavinasab F. Comparison of epinephrine to salbutamol in acute bronchiolitis. Iranian journal of pediatrics. 2012 Jun;22(2):241.
Bloemers BL, Van Furth AM, Weijerman ME, Gemke RJ, Broers CJ, Van Den Ende K, Kimpen JL, Strengers JL, Bont LJ. Down syndrome: a novel risk factor for respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis—a prospective birth-cohort study. Pediatrics. 2007 Oct 1;120(4): e1076-81.
Zorc JJ, Hall CB. Bronchiolitis: recent evidence on diagnosis and management. Pediatrics. 2010 Feb 1;125(2):342-9.
Ralston SL, Lieberthal AS, Meissner HC, Alverson BK, Baley JE, Gadomski AM, Johnson DW, Light MJ, Maraqa NF, Mendonca EA, Phelan KJ. Clinical practice guideline: the diagnosis, management, and prevention of bronchiolitis. Pediatrics. 2014 Nov 1;134(5): e1474-502.
Kabir ML, Haq N, Hoque M, Ahmed F, Amin R, Hossain A, Khatoon S, Akhter S, Shilpi T, Haq R, Anisuzzaman S. Evaluation of hospitalized infants and young children with bronchiolitis-a multi centre study. Mymensingh medical journal: MMJ. 2003 Jul 1;12(2):128-33.
Kuzik BA. Maybe there is no such thing as bronchiolitis. CMAJ. 2016;188(5):351-354.
Qymar K, Skjerven HO, Mikalsen IB. Acute bronchiolitis in infants, a review. Scand J Trauma ResuscEmerg Med. 2014;22:23.
Usman S, Zareen A, Gillani A, Kaleem A, Ali M, Sarwar HA. Comparison of Adrenaline and Salbutamol nebulization in treatment of Children with Bronchiolitis. The Professional Medical Journal. 2019 Sep 10;26(09):1434-9.
Islam MS, Mollah MA, Khanam RO, Chowdhury AS, Rahman MM, Al Baqui SA, Rashid MA. Comparative efficacy of nebulized 7% hypertonic saline versus 0.9% normal saline with salbutamol in children with acute bronchiolitis. Bangladesh J Child Health. 2019;43(2):80-4.
Islam KT, Mollah AH, Matin AB, Begum MA. Comparative efficacy of nebulized 3% hypertonic saline versus 0.9% Normal saline in children with acute bronchiolitis. Bangladesh J Child Health. 2018 Dec 17;42(3):130-7.
Singh C, Angurana SK, Bora I, Jain N, Kaur K, Sarkar S. Clinico demographic profiling of Respiratory syncytial virus infected children admitted in tertiary care hospital in North India. J Family Med Prim Care. 2021;10(5):1975-1980.
Halder AK, Sultana S, Nag BC. Clinico-Epidemiological and Radiological Profile of Bronchiolitis at Shere-E-Bangla Medical College Hospital in Barishal, Bangladesh. Annal of International and Dental Research. 2022;8(1):318-324.