Assessment of Implant Stability in Direct and Indirect Sinus Lift Procedure - A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background and Objective : The sinus lift procedure, also known as maxillary sinus augmentation, aims to augment the bone volume in the maxillary sinus region, facilitating the placement of dental implants with adequate support and stability. The direct sinus lift procedure involves accessing the maxillary sinus through a lateral window approach, followed by elevation of the sinus membrane and placement of bone graft materials. The indirect sinus lift technique involves the use of osteotomes or hydraulic pressure devices to elevate the sinus floor, creating space for bone graft materials without the need for an extensive surgical window. The objective is to systematically review the existing scientific literature in providing a comprehensive, quantitative analysis on effectiveness between direct sinus lift and indirect sinus lift procedure for implant stability.
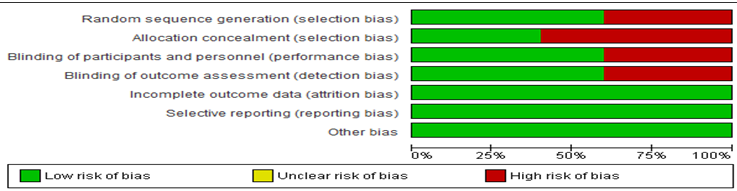
Methods: Review was adhered to Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis (PRISMA) guidelines 2020 and registered in PROSPERO – CRD42024530982. Electronic databases were searched for studies evaluating the effectiveness between direct sinus lift and indirect sinus lift procedure for implant stability and reporting outcomes in terms of overall mean increase in bone height and development of pain, gingival inflammation and swelling. Quality assessment of included studies was evaluated through Cochrane risk of bias (ROB)-2 tool. The standardized mean difference (SMD) and risk ratio (RR) was used as summary statistic measure with random effect model and p value <0.05 as statistically significant through Review manager (RevMan) version 5.3.
Downloads
References
Simon BI, Greenfield JL. Alternative to the gold standard for sinus augmentation: Osteotome sinus elevation. Quintessence Int 2011; 42(9):14-21. 10.22037/ji.v42i10.109.
Irinakis T, Dabuleanu V, Aldahlawi S. Complications during maxillary sinus augmentation associated with interfering septa: a new classification of septa. The Open dentistry J 2017;11(4):140-46. 10.2174/1874210601711010140.
Tatum JH. Maxillary and sinus implant reconstructions. Dent Clin N Am 1986; 30(2): 207-29.
Harris D, Horner K, Gröndahl K, Jacobs R, Helmrot E, Benic GI, et al. E.A.O. Guidelines for the use of diagnostic imaging in implant dentistry 2011. Clin Oral Implants Res 2012; 23: 1243-53. 10.1111/j.1600-0501.2012.02441.x.
Stacchi C, Troiano G, Berton F, Lombardi T, Rapani A, Englaro A, Galli F, Testori T, Nevins M. Piezoelectric bone surgery for lateral sinus floor elevation compared with conventional rotary instruments: A systematic review, meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis. Int J of Oral Implantology. 2020; 1: 13(2). 10.31356/ijoi.v13i2.109.
Temmerman A, Hertelé S, Teughels W, Dekeyser C, Jacobs R, Quirynen M, et al. Are panoramic images reliable in planning sinus augmentation procedures? Clin Oral Implants Res 2011; 22:189-94. 10.1111/j.1600-0501.2010.02000.x.
Stern A, Green J. Sinus lift procedures: an overview of current techniques. Dental Clinics. 2012; 56(1): 219-33. 10.1016/j.cden.2011.09.003.
Bathla SC, Fry RR, Majumdar K. Maxillary sinus augmentation. J Indian Soc Periodontol 2018; 22(6): 468. 10.4103/jisp.jisp23618.
Kim YK, Yun PY, Kim SG, Lim SC. Analysis of the healing process in sinus bone grafting using various grafting materials. Oral Surg Oral Med, Oral Pathol Oral Radiol & Endod 2009; 107(2): 204-11. 10.1016/j.tripleo.2008.07.021.
Summers RB. A new concept in maxillary implant surgery: The osteotome technique. Compendium (Newtown, Pa). 1994; 5(152):154- 156.
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, Shamseer L, Tetzlaff JM, Akl EA, Brennan SE, Chou R. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Int J of surgery. 2020; 88(3): 59-60. 10.1016/j.ijsu.2021.105906.
Corbett MS, Higgins JP, Woolacott NF. Assessing baseline imbalance in randomised trials: implications for the Cochrane risk of bias tool. Res Synthesis Methods. 2014; 5(1): 79-85. 10.1002/jrsm.1090.
DerSimonian R, Laird N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials revisited. Contemp Clin trials. 2015;45: 139-45. 10.1016/j.cct.2015.09.002.
Higgins JP, Thompson SG. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta‐analysis. Statistics
in medicine. 2002;21(11):1539-58. 10.1002/sim.1186.
Daniel D, Rao SG. Evaluation of increase in bone height following maxillary sinus augmentation using direct and indirect technique. J of Dental Implants. 2012; 2(1):26-31. 10.4103/0974-6781.96563.
Pal US, Sharma NK, Singh RK, Mahammad S, Mehrotra D, Singh N, Mandhyan D. Direct vs. indirect sinus lift procedure: A comparison. National J of Maxillofacial Surg 2012; 3(1): 31-7. 10.4103/0975-5950.102148.
Balaji SM. Direct v/s Indirect sinus lift in maxillary dental implants. Ann Maxillofac Surg 2013; 3(2):148-53. 10.4103/2231-0746.119228.
Ghatak D, Tyagi KK, Tiwari E. Implant placement in posterior atrophic maxilla using direct and indirect sinus augmentation-a comparative study. Asian Pac J Health Sci. 2017; 4(1): 201-216. 10.21276/apjhs.2017.4.1.32.
Atiq T, Iqbal S, Rashid W, Ul Ain Q, Asghar I, Javed T. Comparison of Implant Success Rate Between Direct and Indirect Sinus Lift Procedure. Annals of PIMS- Shaheed Zulfiqar Ali Bhutto Medical University. 2022; 18(4): 295-9. 10.48036/apims.v18i4.761.
Khairy N, Abu-Taleb N. CBCT assessment of the integration of xenograft mixed with plasma rich in growth factors (PRGF) in direct maxillary sinus lift surgery: Case series study. Egyptian Dental J. 2023; 69(1): 61-73. 10.21608/edj.2022.156341.2219.
Riben C, Thor A. The maxillary sinus membrane elevation procedure: augmentation of bone around dental implants without grafts—a review of a surgical technique. Int J of dentistry. 2012; 1: 1-9. 10.1155/2012/105483
Kumar H, Agarwal A, Thakur MK. Comparative Evaluations of Direct And Indirect Sinus Lift Technique In Patients Requiring Dental Implants. Int J of Community Health & Medical Res. 2018; 1; 4(4).
Yassin Alsabbagh A, Alsabbagh MM, Darjazini Nahas B, Rajih S. Comparison of three different methods of internal sinus lifting for elevation heights of 7 mm: an ex vivo study. Int J of implant dentistry. 2017; 3: 1-7. 10.1186/s40729-017-0103-5.
Wallace SS, Froum SJ. Effect of maxillary sinus augmentation on the survival of endosseous dental implants. A systematic review. Ann Periodontol 2003; 8(1): 328-43. 10.1902/annals.2003.8.1.328.
Potdukhe SS, Iyer JM, Nadgere JB. Evaluation of implant stability and increase in bone height in indirect sinus lift done with the osseodensification and osteotome technique: A systematic review and meta-analysis. The J of Prosthetic Dentistry. 2023; 5. 10.1016/j.prosdent.2023.04.021.