Manufacture of fibroustructure facemask to protect against coronavirus using electrospinning
Abstract
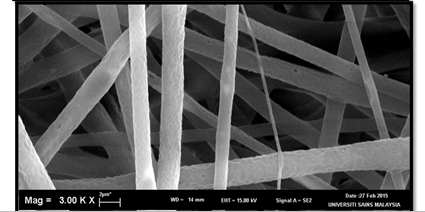
In order to live safely with an exacerbation of the Coronavirus, a face mask must be made with specifications that prevent infection or transmission among people; which is characterized by high efficiency and low cost, and renewable. Fiberstructure widely used in air filtration industry using electrospinning method, where its field is booming in an exceptionally impressive manner. Using a biopolymer as a olyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) to create a facemask will give excellent results because of the solidity and porosity of the polymer in addition to the non-stick feature. During this work, emphasis will be placed on the best method to manufacture the face mask in terms of the solidity and non-stick feature which gives a longer life for facemask. The facemask is quicker and more affordable than delivering a treatment or a counteractant, and furthermore gives the facemask better outcomes against the Coronavirus.
Downloads
References
Laycock, B.; Halley, P.; Pratt, S.; Werker, A.; Lant, P. The chemomechanical properties of microbial polyhydroxyalkanoates. Prog Polym Sci 2013, 38, 536-583.
Philip, S.; Keshavarz, T.; Roy, I. Polyhydroxyalkanoates: biodegradable polymers with a range of applications. Journal of chemical technology & biotechnology: International research in process, Environmental & clean technology 2007, 82, 233-247.
Yu, L.; Dean, K.; Li, L. Polymer blends and composites from renewable resources. Prog Polym Sci 2006, 31, 576-602.
Misra, S.K.; Valappil, S.P.; Roy, I.; Boccaccini, A.R. Polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA)/inorganic phase composites for tissue engineering applications. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 2249-2258.
Ten, E.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, J.; Wolcott, M.P. Mechanical performance of polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA)-based biocomposites. In Biocomposites, Elsevier: 2015; pp. 39-52.
Leung, N.H.; Chu, D.K.; Shiu, E.Y.; Chan, K.-H.; McDevitt, J.J.; Hau, B.J.; Yen, H.-L.; Li, Y.; Ip, D.K.; Peiris, J.M. Respiratory virus shedding in exhaled breath and efficacy of face masks. Nature medicine 2020, 1-5.
Chang, D.; Xu, H.; Rebaza, A.; Sharma, L.; Cruz, C.S.D. Protecting health-care workers from subclinical coronavirus infection. The Lancet Respiratory Medicine 2020, 8, e13.
Organization, W.H. Non-pharmaceutical public health measures for mitigating the risk and impact of epidemic and pandemic influenza: annex: report of systematic literature reviews; World Health Organization: 2019.
Eikenberry, S.E.; Mancuso, M.; Iboi, E.; Phan, T.; Eikenberry, K.; Kuang, Y.; Kostelich, E.; Gumel, A.B. To mask or not to mask: Modeling the potential for face mask use by the general public to curtail the COVID-19 pandemic. Infectious Disease Modelling 2020, 5, 293-308.
Al-Hazeem, N.Z.A. Nanofibers and Electrospinning Method. Nov. Nanomater.-Synth. Appl 2018.
Tebyetekerwa, M.; Xu, Z.; Yang, S.; Ramakrishna, S. Electrospun nanofibers-based face masks. Advanced Fiber Materials 2020, 2, 161-166.
Wang, J.; Kim, S.C.; Pui, D.Y. Investigation of the figure of merit for filters with a single nanofiber layer on a substrate. J. Aerosol Sci 2008, 39, 323-334.
Hsiao, H.Y.; Huang, C.M.; Liu, Y.Y.; Kuo, Y.C.; Chen, H. Effect of air blowing on the morphology and nanofiber properties of blowing‐assisted electrospun polycarbonates. Journal of applied polymer science 2012, 124, 4904-4914.
Maze, B.; Tafreshi, H.V.; Wang, Q.; Pourdeyhimi, B. A simulation of unsteady-state filtration via nanofiber media at reduced operating pressures. J. Aerosol Sci 2007, 38, 550-571.
Zaini, E.; Azaman, M.; Jamali, M.; Ismail, K. Synthesis and characterization of natural fiber reinforced polymer composites as core for honeycomb core structure: A review. Journal of Sandwich Structures & Materials 2020, 22, 525-550.
Liang, M.; Gao, L.; Cheng, C.; Zhou, Q.; Uy, J.P.; Heiner, K.; Sun, C. Efficacy of face mask in preventing respiratory virus transmission: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Travel medicine and infectious disease 2020, 36, 101751.
Al-Hazeem, N.Z.; Ahmed, N.M.; Matjafri, M.; Bououdina, M. Hydrogen gas sensor based on nanofibers TiO 2-PVP thin film at room temperature prepared by electrospinning. Microsystem Technologies 2020, 1-7.
Lim, E.; Seet, R.; Lee, K.H.; Wilder‐Smith, E.; Chuah, B.; Ong, B. Headaches and the N95 face‐mask amongst healthcare providers. Acta Neurologica Scandinavica 2006, 113, 199-202.
Li, Y.; Wong, T.; Chung; Guo, Y.; Hu, J.; Guan, Y.; Yao, L.; Song, Q.; Newton, E. In vivo protective performance of N95 respirator and surgical facemask. American journal of industrial medicine 2006, 49, 1056-1065.
Kumar, A.; Kasloff, S.B.; Leung, A.; Cutts, T.; Strong, J.E.; Hills, K.; Vazquez-Grande, G.; Rush, B.; Lother, S.; Zarychanski, R. N95 mask decontamination using standard hospital sterilization technologies. MedRxiv 2020.
Lee, H.P.; Wang, D.Y. Objective assessment of increase in breathing resistance of N95 respirators on human subjects. Annals of occupational hygiene 2011, 55, 917-921.
Roberge, R.J.; Coca, A.; Williams, W.J.; Palmiero, A.J.; Powell, J.B. Surgical mask placement over N95 filtering facepiece respirators: physiological effects on healthcare workers. Respirology 2010, 15, 516-521.
Roberge, R.J.; Bayer, E.; Powell, J.B.; Coca, A.; Roberge, M.R.; Benson, S.M. Effect of exhaled moisture on breathing resistance of N95 filtering facepiece respirators. Annals of occupational hygiene 2010, 54, 671-677.
SUEN, C.Y.; LEUNG, H.H.; LAM, K.W.; Karen, P.H.; CHAN, M.Y.; KWAN, J.K.C. Feasibility of Reusing Surgical Mask Under Different Disinfection Treatments. medRxiv 2020.
De Vrieze, S.; Van Camp, T.; Nelvig, A.; Hagström, B.; Westbroek, P.; De Clerck, K. The effect of temperature and humidity on electrospinning. Journal of materials science 2009, 44, 1357-1362.
Al-Hazeem, N.Z.; Ahmed, N.M. Effect of Addition of Polyaniline on Polyethylene Oxide and Polyvinyl Alcohol for the Fabrication of Nanorods. ACS Omega 2020.
Cui, W.; Li, X.; Zhou, S.; Weng, J. Investigation on process parameters of electrospinning system through orthogonal experimental design. Journal of applied polymer science 2007, 103, 3105-3112.
Li, Z.; Wang, C. Effects of working parameters on electrospinning. In One-dimensional nanostructures, Springer: 2013; pp. 15-28.
Park, H.-S.; Park, Y.O. Filtration properties of electrospun ultrafine fiber webs. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2005, 22, 165-172.
Gibson, P.; Schreuder-Gibson, H.; Rivin, D. Transport properties of porous membranes based on electrospun nanofibers. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects 2001, 187, 469-481.
Robinson, M.; Franklin, H. The pressure drop of a fibrous filter at reduced ambient pressures. J. Aerosol Sci 1972, 3, 413-427.