Post recovery Covid-19 patients: Factor affecting oxygen saturation and complication in them.
Abstract
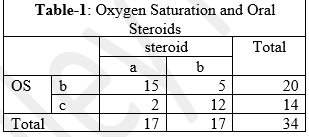
Oxygen saturation is a measure of how much hemoglobin is currently bound to oxygen compared to how much remains unbound. Oral steroids rapidly reduce the inflammation and are associated with rapid rise in oxygen saturation. The post recovery complications vary from Relapsing fever to wakefulness to tiredness. Proning has been found effective in increasing the oxygen saturation of the patient. The objectives of this study is to determine the effect of steroids, antifungals, proning and breathing exercises on post recovery oxygen saturation in COVID- 19 patients and to find the common post recovery complaints/complications in the COVID-19 patients. It was a cross- sectional study. The study had 34 participants. All the participants had history of COVID-19 infection. 31 reported post recovery tiredness. 13 practiced proning in the recovery period while, 12 practiced breathing exercises. The oxygen saturation was compared with those who took oral steroids by Pearson Chi-Square test the P value was found to be 0.000 thus there is a significant difference between the oxygen saturation of those who received oral steroids and those who did not. There is a significant association between use of antifungal and oxygen saturation post recovery with Pearson Chi- square p value 0.003. The Pearson Chi-Square test gives a p value of 0.000 thus there is a significant association between post recovery oxygen saturation and proning. The Pearson Chi-Square test gives a P value of 0.003 thus there is a significant association between post recovery oxygen saturation and breathing exercises.
Downloads
References
Brant B. Hafen, Sandeep Sharma. Oxygen Saturation. StatPearls [Internet], Accessed on 2021 May 8. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK525974/#_NBK525974_pubdet_.
Underlying Medical Conditions: Information For Healthcare Providers. Centers For Disease Control and Prevention. Accessed on 2021 May 9. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/hcp/clinical-care/underlyingconditions.html
B Ravishankar, VJ Shukla. Indian Systems of Medicine: A Brief Profile. AJTCAM, 2007; 4(2). 2007 Feb 16; 319-337. https://doi.org/10.4314/ajtcam.v4i3.31226.
Ayers, J.S. A Metabolic Handbook for COVID-19. Nat Metlab, Edition 2, 2020 Jun 30; 572-585. http://doi.org/10.1038/s42255-020-0237-2.
Mayo Clinic Staff, COVID-19 (coronavirus): Long-term effects, MFMER [Internet], Accessed on 2021 May 8. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/coronavirus/in-depth/coronavirus-long-term-effects/art-2049051#:~:text=Imaginf%20tests%20taken%20months%20after,Lungs.
Simin Jahani, Ziba Hajivand Soleymani, Marziyeh Asadizaker, Farhad Soltani, Bahman Cheraghian. Determination of effects of prone position on oxygenation in patients with acute respiratory failure under mechanical ventilation in ICU. JML,2018 Oct-Dec; 11(4). 2018 Aug 18; 274-280. https://doi.org/10.25122/jml-2018-0028.
Narges Meftahi, Soha Bervis, Shohreh Taghizadeh, Farahnaz Ghaffrinejad. The effect of lying in prone position on blood pressure and heart rate with and without massage. JRSR, 1. 2014 Sep; 40-43. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/267043007_The_Efect_of_Lying_in_Prone_Position_on_Blood_Pressure_and_Heart_Rate_with_and_without_Massage.
Lahav DZ, Picard E, Mimouni F, Joseph L, Goldberg S. The effect of fever on blood oxygen saturation in children. Harefuah, 2015 Mar; 154(3). 2015 Mar; 162-165. [PubMed. PMID: 25962244]
Shmule Goldberg, Shmule Heitner, Francis Mimouni, Leon Joseph, Reuben Bromiker, Elie Picard. The influence of reducing fever on blood oxygen saturation in children. Eur J Pediatr, 2018 Jan; 177(1). 2017 Nov 3; 95-99. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-017-3037-2. [PubMed. PMID: 29101451]
Jerrold S. Petrofsky, Michael S. Laymon,Iman Akef Khowailed, Stacy Fisher, Andrew Mills. The effect of BMI on Oxygen Saturation at rest and during mild walking. JAMS, 4(2). 2016 Aug 2016; 1-8. https://touroscholar.touro.edu/chhs_pubs/1/.
Alireza Abdi, Milad Jalilian, Pegah Ahmadi Sarbarzeh, Zeljko Vlaisavljevic. Diabetes and COVID-19: Asystematic review on current evidences. DRCP, 2020 Aug. 2020 Jul 22: 166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108347 [PubMed. PMID: 32711003]
Aditya Moorthy, Rohith Gaikwad, Shreya Krishna, Raghuraj Hedge, KK Tripathi, Preeti G Kale, P Subramanya Rao, Deepak Haldipur, Krishnamurthy Bonthaya. SARS-CoV-2, Uncrontrolled Diabetes and Corticosteroids- An unholy Trinityin invasive fungal infection of the maxillofacial region? A retrospective, Multicentric Analysis. J Maxilliofac. Oral Surg., 2021. 2021 Mar 6; 1-8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12663-021-01532-1.
Dorothea Closhen, Kristin Engelhard, Frank Dette, Christian Werner, Patrick Schramm. Changes in cerebral oxygen saturation following prone prone positioning for orthopaedic surgery under general anaesthesia: a prospective observational study. Eur J Anaesthesiol, 2015 Jun; 32(6). 2015 Jun 1; 381-386. https://doi.org/10.1097/EJA.0000000000000259. [PubMed. PMID: 25828358]