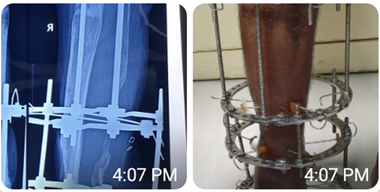
Evaluation of illizarov technic in treating tibial open fractures: An observational study
Abstract
Introduction: Illizarov technique is a versatile method of treating open tibial fractures after debridement and open reduction. Tibial open fractures are usually classified into Type I, II, IIIA, IIIB and IIIC. Illizarov method has many advantages and features for such fracture treatment. But in Bangladesh, we have not enough research-oriented information regarding this treatment method.
Aim of the study: This study aimed to assess the Ilizarov technique in treating tibial open fractures.
Methods: This observational prospective study was conducted in the Department of Orthopedics of TMSS Medical College, Bogura, Bangladesh and 3 associated private clinics during the period from January 2018 to December 2021. In total 23 patients with tibial open fractures were confirmed as the study subjects. Before starting this 3 year in3-yeartion, proper written consent of the participants was taken and this study was approved by the ethical committee of the mentioned hospital and clinics. A semi-structured; pre-designed questionnaire was used in collecting patient data. All the data were processed, analyzed and disseminated by using MS Office and SPSS version 23.
Results: In this study, we found highest 65% of participants were injured from road traffic accidents (RTA) followed by 26% from general falls and the rest 9% from a sports injury as the mode of injury. The total treatment duration with the fixator was 12-23 weeks with an average of 16 weeks. The operation time ranged from 90 minutes to 120 minutes. As per the Karlstrom and Olerud criteria, the highest 70% of patients got ‘excellent’ results. Besides this, 17%, 9% and 4% of patients got ‘good’, ‘fair’ and ‘poor’ results respectively.
Conclusion: In our study, we found some excellent features the of Ilizarov induced method in the treatment of open fractures of tibia. We would like recommend more use of Ilizthe arov technic in the field of Orthopaedics.
Downloads
References
Court-Brown CM, McBirnie J. The epidemiology of tibial fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1995; 77: 417-21.
Tornetta P, Bergman M, Watnik N, Berkowitz G, Steuer J. Treatment of grade-IIIb open tibial fractures. A prospective randomized comparison of external fixation and non-reamed locked nailing. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1994; 76: 13-9.
Hutchinson AJP, Frampton AE, Bhattacharya R. Operative fixation for complex tibial fractures. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2012; 94:34-8.
Gustilo RB, Anderson JT. Prevention of infection in the treatment of one thousand and twenty-five open fractures of long bones: retrospective and prospective analyses. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1976; 58: 453-8.
Wani N, Baba A, Kangoo K, Mir M. Role of early Ilizarov ring fixator in the definitive management of type ІІ, ІІІA and ІІІB open tibial shaft fractures. Int Orthop 2011; 35:915-23. [20445978] [http://dx.doi.org/10.100 7/s00264-010-1023-7]
Hasankhani E, Payvandi MT, Bir- jandinejad A. The Ilizarov ring ex- internal fixator in complex open fractures of the tibia. Eur J Trauma 2006; 32:63-8. [http://dx.doi.org/10. 1007/s00068-005-0031-6]
Papaioannou N, Mastrokalos D, Papagelopoulos PJ, Tyllianaksi M, Athanassopoulos J, Nikiforidis PA. Nonunion after primary treatment of the tibia fractures with external fixa- tor. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 2001; 11:231-35. [http://dx.doi.org/1 0.1007/BF01686895]
Gustilo RB. Management of open fractures, in Gustilo RB (Ed.). Orthopaedic Infection, diagnosis and treatment, 1st edition (Philadelphia:WB Saunders Company, 1989) 87-89.
Paul, H Kim; Seth, S Leopold (9 May 2012). "Gustilo-Anderson Classification". Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research. 470 (11): 3270–3274. doi:10.1007/s11999-012-2376-6. PMC 3462875. PMID 22569719.
"Ovid: Externer Link". ovidsp.tx.ovid.com. Retrieved 2017-11-10.
Trafton PG. Tibial shaft fractures, in Browner BD, Jupiter JB, Levine AM, Krettek C (Eds.). Skeletal trauma: basic science, management and reconstruction, 4th edition, Vol. 2 (Philadelphia: Saunders, 1998) 2319-2451.
Golyakhovsky V, Frankel VH. Operative manual of Ilizarov techniques, (New Delhi: Jaypee Brothers, 1986).
Tucker HL, Kendra JC, KInnebrew TE. Management of unstable open and closed tibial fractures using Ilizarov method, Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research, 280, 1992, 125-135.
Shtarker H David, R, Stolero J, Grimberg B, Soundry M. Treatment of open tibial fractures with primary suture and Ilizarov fixation, Clinical Orthopaedics an Related Research, 335, 1997, 268-274.
Keating JF, Obrier PF, Blachut PA, Meck RN, Broekhuse HM. Locking intramedullary nailing with and without reaming for open fracture of the tibial shaft, The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery, 79 A, 1987, 334-341.
Hulth A. Basic science and pathology, the current concept of fracture healing: Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research, 249, 1989, 265-285.