Effect of Momordica charantia (korola) in global cerebral ischemia-induced neuronal damage in rat brain
Abstract
Background: Stroke is primarily a cardiovascular disease with a neurological outcome. Prophylactic neuroprotection might be a useful treatment approach with better outcome than current options. Momordica charantia (Korola) fruit juice has been shown different therapeutic effects including neuroprotection.
Objective: The objective of the study was performed to evaluate neuroprotective effect of Momordica charantia fruit juice in global cerebral ischemia induced neuronal damage in rats.
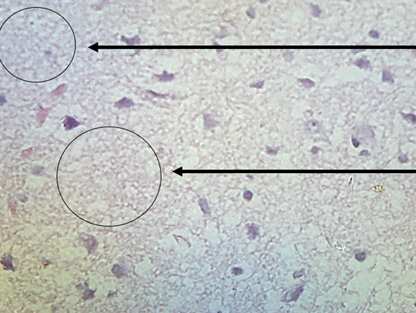
Methodology: Global cerebral ischemia was produced surgically by ligating bilateral and unilateral common carotid artery. Fresh raw juice of Momordica charantia (2-2.5 ml/rat/day) was given to experimental group starting one month before and continued up to two weeks after surgery. Forty wester Kyoto rats were recruited for experiment and divided into two groups. Neuroprotective role was measured with the Histopathological assessment of decapitated rat brain in terms of unaffected neuronal cell density and necrotic foci per high power field (HPF). The data analysis was done by unpaired t- test with the software SPSS version 17.0.
Results: Among 40 rats, 24 rats were alive until completion of experiment. The rats under experimental group who got Momordica charantia fruit juice had significantly more neuronal cell density (p=0.001) and less necrotic foci (p=0.001) compared with control group.
Conclusion: In this study, we found that Momordica charantia fruit juice has neuroprotective activity in global cerebral ischemia induced neuronal damage in rat brains. Since herbal drugs have been accepted widely in the recent years because of its’ relative higher therapeutic window, less serious side effects, and economical, Momordica charantia fruit juice might be the alternative of other synthetic neuroprotective agents in global cerebral ischemia-induced neuronal damage. However, in vivo study is warranted to establish this relation.
Downloads
References
Green, A.R. (2008). Pharmacological approaches to acute ischaemic stroke: reperfusion certainly, neuroprotection possibly. British Journal of Pharmacology, vol. 153, pp.325 -338.
Fisher, M. and Schaebitz, W. (2000). An overview of acute stroke therapy past, present, and future. JAMA Internal Medicine, vol. 160, pp.3196-3206.
Jonas, S. (1995). Prophylactic Pharmacologic neuroprotection against focal cerebral ischemia. Ann N Y Acad Sci, vol. 765, pp.21-25.
Chaudhary, G., Sinha, K., Gupta, Y.K. (2003). Protective effect of exogenous administration of alpha¬tocopherol in middle cerebral artery occlusion model of cerebral ischemia in rats. Fundamental Clinical Pharmacology, vol. 17, pp.703-707.
Perttu, J., Lindsberg, Risto, O., Roine, A., Talisumak, T., Sairanen, T. et al. (2000). The future of stroke treatment. Stroke, vol. 19, pp.495-510.
Malik, A.Z., Singh, M., Sharma, P.L. (2011). Neuroprotective effect of Momordica charantia in global cerebral cerebral ischemia and reperfusion induced neuronal damage in Diabetic mice. Journal of ethnopharmacology. vol. 133, pp.729-734.
Farkas, E., Paul, G.M., Luiten, Bari, F. (2007). Permanent bilateral common carotid artery occlusion in the rat: A model for chronic cerebral hypoperfusion related neurodegenerative diseases. Brain research review, vol. 54, pp.162-180.
Raghavendra, M., Trigunayat, A., Singh, R.K., Mintra, S., Goel, R.K., Acharya, S.B. (2007). effect of Ethanolic extract of root of pongamia Pinnata (L) pierre on oxidative stress, behavioral and histopathological alterations induced by cerebral ischemia- reperfusion and long-term hypo perfusion in rat. Indian journal of experimental biology, vol. 45, pp.868-876.
Saeed, M.K., Shahjadi, I., Ahmed, I., Ahmed, R., Shahjad, K., Ashraf, M. et al. (2010). Nutritional analysis and antioxidant activity of bitter gourd from Pakistan. pharmacology online, vol. 1, pp. 252-260.
Mohamed, H.E., El-Swefy, S.E., Hasan, R.A., hasan, A.A. (2014). Neuroprotective effect of Resveratrol in Diabetic cerebral ischemic- reperfused rats through regulation of inflammatory and apoptotic events. Diabeology and metabolic syndrome, vol.6, pp.88-97.