Efficacy of Ibuprofen and Paracetamol in the management of hemodynamically significant patent ductus arteriosus in preterm babies.
Abstract
Background: Preterm babies are at high risk for many complications and multiple morbidities. A patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) is one of the major problem which causes significant alteration in hemodynamics. There are various modalities of closing hemodynamically significant PDA such as surgical ligation and closure by various pharmacological agents like Indomethacin, Ibuprofen and Paracetamol. The present study was performed to explore the use of oral Indomethacin, Ibuprofen and Paracetamol in preterm babies in a rural based tertiary care center which has its own limitations.
Aims & Objectives: To compare the efficacy, side-effects and outcome of Ibuprofen and Paracetamol in the management of hemodynamically significant Patent Ductus Arteriosus in preterm babies.
Material and Methods: All neonates admitted at Pravara Rural Hospital during December 2020 to April 2022 with birth weight < 1800 grams were included in our study. All babies fulfilling the inclusion criteria were given either oral ibuprofen or paracetamol and result to each of these along with side effects was monitored for.
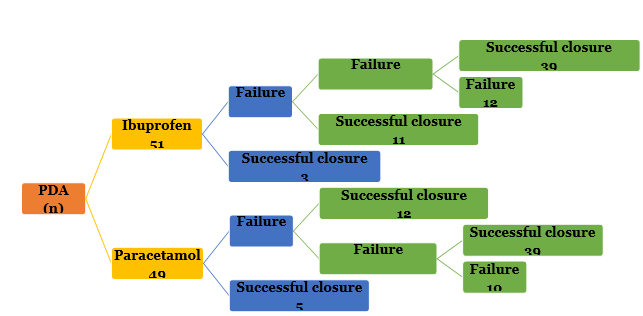
Results: PDA closure rate was maximal with oral paracetamol though the difference in closure rate of these drugs was statistically not significant. Preterm with gestational age lesser than 32 weeks showed better results with oral ibuprofen. Preterm with gestational age more than 32 weeks showed better closure rates with oral paracetamol.
Conclusion: This study demonstrates that Patent Ductus Arteriosus closure in preterm babies can be attempted with oral use of any of these drugs i.e Ibuprofen and Paracetamol. In our study, maximal success was obtained with use of oral paracetamol though the difference in closure rate of both drugs was statistically not significant.
Downloads
References
Sophie Vanhaesebrouk, Inge Zonnenberg, Piet Vandervoort, Els Bruneel, Marie- Rose Van Hoestenberghe, Claire Theyskens. Conservative treatment for patent ductus arteriosus in the preterm. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2007 Jul;92(4) :F244-F247
Se In Sung, Yun Sil Chang, Ji Young Chun, Shin Ae Yoon, Hye Soo Yoo, So Yoon Ahn, Won Soon Park. Mandatory Closure Versus Nonintervention for Patent Ductus Arteriosus in Very Preterm Infants. JPediatr 2016;177:66-71
Herman K, BoseC, LewisK, LaughonM. Spontaneous closure of the patent ductus arteriosus in very low birth infants following discharge from the neonatal unit. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2009 Jan;94(l):F48-50
Nemerofsky SL, Parravicini E, Bateman D, Kleiman C, Polin RA, Lorenz JM. The ductus arteriosus rarely requires treatment in infants >1000grams. Am J Perinatol 2008 Nov;25(10): 661-666
Domelles LV, et al. Comparison of two dose regimens of ibuprofen for the closure of patent ductus arteriosus in preterm newborns . J Pediatr (Rio J).2016.May-June
Olukman O, et al . Comparison of oral and intravenous ibuprofen for medical closure of patent ductus arteriosus: which one is better ? Congenit Heart Dis.2012.Nov-Dec[Pubmed] PMID:22613269
Hammerman C, et al .Ductal closure with paracetamol :a surprising new approach to patent ductus arteriosus treatment. Pediatrics 2011 [Pubmed] PMID:22065264
Bharathi Balachander, Nivedita Mondal, Vishnu Bhat, Bethou Adhisivam, Mahesh Kumar, Santhosh Satheesh & Mahalakshmi Thulasingam (2020) Comparison of efficacy of oral paracetamol versus ibuprofen for PDA closure in preterms – a prospective randomized clinical trial, The Journal of Maternal-Fetal & Neonatal Medicine, 33:9, 1587-1592, DOI: 10.1080/14767058.2018.1525354
Lu J, Li Q, Zhu L, Chen C, Li Z. Oral ibuprofen is superior to oral paracetamol for patent ductus arteriosus in very low and extremely low birth weight infants. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 Aug;98(31):e16689. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000016689.
El-Mashad, A.ER., El-Mahdy, H., El Amrousy, D. et al. Comparative study of the efficacy and safety of paracetamol, ibuprofen, and indomethacin in closure of patent ductus arteriosus in preterm neonates. Eur J Pediatr 176, 233–240 (2017).
Dani, C., Lista, G., Bianchi, S. et al. Intravenous paracetamol in comparison with ibuprofen for the treatment of patent ductus arteriosus in preterm infants: a randomized controlled trial. Eur J Pediatr 180, 807–816 (2021).
Dang D, Wang D, Zhang C, Zhou W, Zhou Q, Wu H. Comparison of oral paracetamol versus ibuprofen in premature infants with patent ductus arteriosus: a randomized controlled trial. PLoS ONE. (2013) 8:e77888. 10.1371/journal.pone.0077888
Oncel MY, Yurttutan S, Erdeve O, Uras N, Altug N, Oguz SS, et al. Oral paracetamol versus oral ibuprofen in the management of patent ductus arteriosus in preterm infants: a randomized controlled trial. J Pediatr. (2014) 164:510–14.e1. 10.1016/j.jpeds.2013.11.008
Bagheri MM, Niknafs P, Sabsevari F, Torabi MH, Bahman Bijari B, Noroozi E, et al.. Comparison of oral acetaminophen versus ibuprofen in premature infants with patent ductus arteriosus. Iran J Pediatr. (2016) 26:3975. 10.5812/ijp.3975
Yang B, Gao X, Ren Y, Wang Y, Zhang Q. Oral paracetamol vs. oral ibuprofen in the treatment of symptomatic patent ductus arteriosus in premature infants: a randomized controlled trial. Exp Ther Med. (2016) 12:2531–6. 10.3892/etm.2016.3676
Kumar A, Gosavi RS, Sundaram V, Oleti TP, Krishnan A, Kiran S, et al.. Oral paracetamol vs oral ibuprofen in patent ductus arteriosus: a randomized, controlled, noninferiority trial. J. Pediatr. (2020) 222:79–84. 10.1016/j.jpeds.2020.01.058.