Clinico-etiologic profile of acute viral hepatitis in children presenting to tertiary care center of rural Maharashtra.
Abstract
Background: Acute Viral hepatitis is defined as an infection of the hepatic tissue due to hepatotropic and/or non hepatotropic viruses causing hepatocellular inflammation which is a self-limiting illness usually resolving completely within 4-6 weeks of time. The clinical band of acute viral hepatitis ranges from subclinical disease to fulminant hepatic failure. We conducted this study to ascertain the Clinico- etiologic profile along with the outcome of acute viral hepatitis in children belonging to rural western Maharashtra.
Method: A retrospective observational study was conducted in department of Pediatrics after ethical approval from the institution and included children from 6 months to 12 years of age and was conducted during November 2021 and included patients admitted to Pravara Rural Hospital during October 2020 to October 2021.
A total of 28 children were clinically diagnosed with acute viral hepatitis were included in the study and data was obtained and analyzed using appropriate statistical tool.
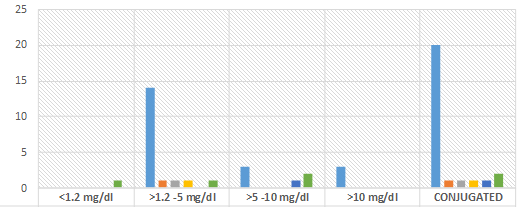
Results: Among 28 cases 18(64.28%) were boys and 10 were girls (35.71%). Mean age group was 7.03± 2.54 years. Virology marker revealed 20 (71%) cases positive for hepatitis A(HAV), 1(3%) case positive for hepatitis E (HEV), and co-infection with HAV and HEV in 1(4%) case, no specific etiology was detected in 4(14%) cases, 1(4%) case positive for hepatitis B and hepatitis C cases were detected. Jaundice was the most common (100%) presenting complaint, followed by fever (92%), pain abdomen (85%), high colored urine (72%). Conjugated hyperbilirubinemia was detected in all (100%) the HAV, HEV positive cases, hepatic enzymes raised above 5 times of normal limit in all the HAV, HEV positive cases. INR more than 2.5 was noticed among 3 HAV positive cases (10.71%). Acute liver failure was seen in 2 children, and both the cases died after 3-4 days of PICU admission.
Conclusion: Hepatitis A is most common cause of acute viral hepatitis in pediatrics population. Hepatitis E infection leads a more severe clinical course than HAV infection.
Downloads
References
Girish N., Sunil B., Ranganatha A. Devaranavadagi A clinical study of viral hepatitis in children: a prospective hospital-based study. International Journal of Contemporary Pediatrics.2018 Mar;5(2): 563-568
Sathiyasekaran M. Viral Hepatitis. In; A Parthasarathy (eds) IAP TEXTBOOK OF PEDIATRICS. Sixth edition. New Delhi; Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers (P) Ltd. 2016. p631-634.
Jensen M.K., Balistreri W. F. Viral Hepatitis. In; Kliegman R M,Stanton B F ,St Geme J W,Schor N F,Behrman R E(eds) Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics. First South Asia Edition. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 2016.p1942-1953.
Behera MR, Patnaik L. Clinicobiochemical profile and etiology of acute viral hepatitis in hospitalized children: A study from Eastern India. Indian J Child Health. 2016; 3(4):317-320.
Jagadisan B. Acute Hepatitis. In; Gupta P, Ramji S, Lodha R (eds) PG Textbook of Pediatrics. 2nd Edition.New Delhi; The Health Sciences Publisher; 2018.p1762-1765.
Poddar U, Thapa BR, Prasad A, Singh K. Changing Spectrum of Sporadic Acute Viral Hepatitis in Indian Children. Journal of Tropical Pediatrics. 2002 August: Vol. 48.
Jabbar A, Pathan M. Clinical Profile of Viral Hepatitis at a Tertiary Care Centre in Rural Maharashtra: An Observational Study. IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences. 2015 oct. PP 26-28.
Kamath SR, Sathiyasekaran M, Raja TE, Sudha L. Profile of viral hepatitis A in Chennai. Indian Pediatrics. 2009;46(7):642-3.
Zanetti AR, Romano L, Zappa A, Velati C (2006) Changingn patterns of hepatitis B infection in Italy and NAT testing for improving the safety of blood supply. J Clin Virol 36(1): S51-S55
Centre for disease control and prevention (2004) Acute hepatitis B among children and adolescents, United States 53(43):1015-18.
Lisotti A, Azzaroli F, Buonfiglioli F, Montagnani M, Alessandrelli F, et al. (2008) Lamivudine treatment for severe acute HBV hepatitis. Int J Med Sci 5(6):309-12.
Parekh Z, Modi R, Banker D. Clinical study of hepatitis in children with special reference to viral markers. NHL J Med Sci. 2013;2(1):23-7.
Das DS. Clinical Profile of Acute Viral Hepatitis in Children – In Southern Assam. Journal of Medical Science And clinical Research. 2021 Mar 23;09(03).
Sravanthi K. A study of clinical profile of viral hepatitis A and E among children at tertiary care centre. MedPulse International Journal of Pediatrics. 2021;19(2):30–2.
S. Rewatkar S, D. Shendre S, Agarwal P, Loni R, Ray M. Etiology of hepatitis in children. International Journal of Contemporary Pediatrics. 2017 Oct 24;4(6):2130.
Sharma CM, Gupta S, Aggarwal B, Chaudhary P. Acute viral hepatitis in children: a prospective hospital based study. International Journal of Contemporary Pediatrics. 2020 Jul 22;7(8):1681.
International Travel and Health Chapter 6 -Vaccine-preventable diseases and vaccines [Internet]. [cited 2022 Sep 30]. Pg.10-13 Available from: https://cdn.who.int/media/docs/default-source/travel-and-health/9789241580472-eng-chapter-6.pdf?sfvrsn=8c1a400c_9