Progression & prognosis of Covid-19 patients having diabetes mellitus
Abstract
Background: Diabetes patients experience a variety of internal health issues, including immune deficiencies, inflammatory storms, hyperglycemia, coagulation risks, and elevated levels of ACE2 receptors. They also suffer from various illnesses like high blood pressure, cardiovascular disease, kidney problems, visual issues, and a host of others. None of these factors raise the chance of contracting SARS-CoV-2. However, once they are infected, the condition worsens to the point that the death rate is high.
Objective: This study aimed to examine the severity of symptoms between COVID-19 participants with and without diabetes.
Methods: A total of 347 patients with confirmed SARS CoV-2 were selected by a purposive sampling method for this retrospective, single-center study that took place from June 1, 2020, to August 31, 2020, at the Department of Medicine, TMSS Medical College, and Rafatullah Community Hospital, Bogura, Bangladesh. We investigated and compared their sociodemographic information, clinical traits, morbidities, lab results, and CT scan results. The study was approved by the ethical committee of the mentioned hospital. All of the patients tested positive for COVID 19. Patients with a COVID 19 negative result and those younger than 18 years old were, however, eliminated based on the study's exclusion criteria.
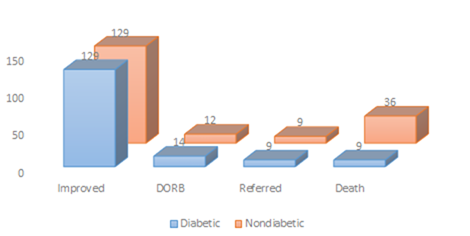
Results: Diabetes patients experienced worse hospital outcomes, including a death rate of 19.4% (p=0.002163), and longer hospital stays (p = 0.0001) compared to non-diabetic patients. Additionally, diabetic patients got more oxygen therapy (32 hours, p 0.05), injectable antiviral drugs (161, p 0.05), and low molecular weight heparin (105, p 0.05) than non-diabetics. These findings suggest that diabetes affects the prognosis of COVID 19.
Conclusion: Diabetes worsens the prognosis and is a risk factor for the Covid-19 symptoms' quick progression. Therefore, individuals with Covid-19 infection and diabetes should receive additional attention because they could deteriorate at any time.
Downloads
References
Mahase E. Covid-19: WHO declares pandemic because of “alarming levels” of spread, severity, and inaction. BMJ. 2020;368: m1036.
Meo SA, Abukhalaf AA, Alomar AA, Alessa OM, Sami W, Klonoff DC. Effect of environmental pollutants PM-2.5, carbon monoxide, and ozone on the incidence and mortality of SARS-COV-2 infection in ten wildfires affected counties in California. Science of the Total Environment. 2021 Feb 25;757:143948.
Cuba K, Imai Y, Rao S, Gao H, Guo F. Guan Bet al. Un papel crucial de la enzima convertidora de angiotensina 2 (ACE2) en la lesión pulmonar inducida por coronavirus del SARS. Nat. Med. 2005;11(8):875-9.
Patel VB, Zhong JC, Grant MB, Oudit GY. Role of the ACE2/angiotensin 1–7 axis of the renin–angiotensin system in heart failure. Circulation research. 2016 Apr 15;118(8):1313-26.
Tipnis SR, Hooper NM, Hyde R, Karran E, Christie G, Turner AJ. A human homolog of angiotensin-converting enzyme: cloning and functional expression as a captopril-insensitive carboxypeptidase. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2000 Oct 27;275(43):33238-43.
Huang I, Lim MA, Pranata R. Diabetes mellitus is associated with increased mortality and severity of disease in COVID-19 pneumonia–a systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression. Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews. 2020 Jul 1;14(4):395-403.
Papadokostaki E, Tentolouris N, Liberopoulos E. COVID-19, and diabetes: What does the clinician need to know? Primary care diabetes. 2020 Oct 1;14(5):558-63.
Shaw JE, Sicree RA, Zimmet PZ. Global estimates of the prevalence of diabetes for 2010 and 2030. Diabetes research and clinical practice. 2010 Jan 1;87(1):4-14.
Shah BR, Hux JE. Quantifying the risk of infectious diseases for people with diabetes. Diabetes care. 2003 Feb 1;26(2):510-3.
Muller LM. J, Gorter KJ, Hak E, Goudzwaard WL, Schellevis FG, Hoepelman AIM, et al. Increased Risk of Common Infections in Patients with Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Clin Infect Dis. 2005 Aug 1;41(3):281-8.
Maddaloni E, Buzzetti R. Covid‐19 and diabetes mellitus: unveiling the interaction of two pandemics. Diabetes/metabolism research and reviews. 2020 Oct;36(7):e33213321.
Singh AK, Gupta R, Ghosh A, Misra A. Diabetes in COVID-19: Prevalence, pathophysiology, prognosis and practical considerations. Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews. 2020 Jul 1;14(4):303-10.
Guo W, Li M, Dong Y. Diabetes is a risk factor for the progression and prognosis of COVID-19 [published online March 31, 2020]. Diabetes Metab Res Rev.
Fadini GP, Morieri ML, Longato E, Avogaro DA. Prevalence and impact of diabetes among people infected with SARS-CoV-2. Journal of endocrinological investigation. 2020 Jun;43(6):867-9.
Yang J, Zheng YA, Gou X, Pu K, Chen Z, Guo Q, Ji R, Wang H, Wang Y, Zhou Y. Prevalence of comorbidities and its effects in patients infected with SARS-CoV-2: a systematic review and meta-analysis. International journal of infectious diseases. 2020 May 1;94:91-5.
Grasselli G, Zangrillo A, Zanella A, Antonelli M, Cabrini L, Castelli A, Cereda D, Coluccello A, Foti G, Fumagalli R, Iotti G. Baseline characteristics and outcomes of 1591 patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 admitted to ICUs of the Lombardy Region, Italy. Jama. 2020 Apr 28;323(16):1574-81.
Yang JK, Feng Y, Yuan MY, Yuan SY, Fu HJ, Wu BY, Sun GZ, Yang GR, Zhang XL, Wang L, Xu X. Plasma glucose levels and diabetes are independent predictors for mortality and morbidity in patients with SARS. Diabetic medicine. 2006 Jun;23(6):623-8.
Guzmán-Flores JM, López-Briones S. Cells of innate and adaptive immunity in type 2 diabetes and obesity. Gaceta medica de Mexico. 2012;148(4):381-9.
Shu CJ, Benoist C, Mathis D. The immune system's involvement in obesity-driven type 2 diabetes. InSeminars in immunology 2012 Dec 1 (Vol. 24, No. 6, pp. 436-442). Academic Press.
Wang D, Hu B, Hu C, Zhu F, Liu X, Zhang J, Wang B, Xiang H, Cheng Z, Xiong Y, Zhao Y. Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus–infected pneumonia in Wuhan, China. Jama. 2020 Mar 17;323(11):1061-9.
World Medical Association. World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki. Ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects. Bulletin of the World Health Organization. 2001;79(4):373.
Voigt P, von dem Bussche A. Enforcement and fines under the GDPR. InThe EU General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) 2017 (pp. 201-217). Springer, Cham.