Efficacy Of Helicobacter Pylori Eradication In Helicobacter Pylori Positive Functional Dyspepsia Patients-A Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial
Abstract
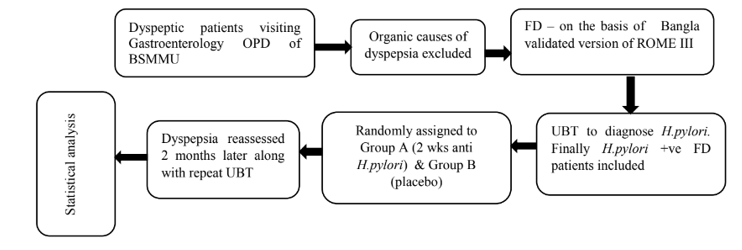
Multiple etiopathogenesis have been proposed for functional dyspepsia. But no conclusive mechanisms have been established yet. Many studies reported that H. pylori produce dyspeptic symptoms without any macroscopic lesion in the gastroduodenal mucosa. Some studies also reported that eradication of H. pylori relieves the symptoms of functional dyspepsia. The main objective of this double blind randomized placebo controlled clinical trial was to see the response of H. pylori eradication in the management of ‘H. pylori positive functional dyspepsia’. We conducted the study on H. pylori positive functional dyspepsia patients visiting the gastroenterology OPD and see the effects of H. pylori eradication on their symptom resolution. Consecutive 59 H. pylori positive functional dyspepsia patients were randomly assigned to receive either Anti H. pylori therapy (Levofoxacin, Amoxicillin and Omeprazole) or placebo for 14 days. H. pylori status was assessed by 13C urea breath test for inclusion into the study and 2 months later for eradication status along with symptom resolution. 23 patients receiving Anti H. pylori therapy and 17 receiving placebo were available for analysis. Two months after completion of therapy 56.5% patients resolved their symptoms who received Anti H. pylori therapy. On the other hand, 47.1% patients who received placebo relieved their dyspeptic symptoms. Dyspeptic symptom resolution was also not statistically significant when comparison made between H. pylori eradicated and non- eradicated subjects irrespective of their treatment regimen (p=0.102). So in this study we found that there is no relationship between H.pylori eradication and resolution of dyspeptic symptoms in patients with functional dyspepsia.
Downloads
References
Baron, JH, Watson, F, and Sonnenberg, A. (2006) ‘Three centuries of stomach symptoms in Scotland’, Alimentary Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 24, pp. 821-29.
Tack, J. (2016) ‘Dyspepsia’. In: Feldman M et al. Sleisenger and Fordtran’s Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease pathophysiology/Diagnosis/management. Philadelphia: Elseviere saunders.
Ford, AC, and Moayyedi, P. (2013) ‘Dyspepsia’, British Medical Journal, 347:f5059.
Chowdhury, J. (2008) Study of the prevalence of dyspepsia in the adult population in a rural community of Bangladesh. Unpublished MD thesis. Bangabandhu Sheikh Mujib Medical University.
Pervin, I, Rahman, MM, Saha, M, and Hasan, MQ. (2014) ‘Prevalence of irritable bowel syndrome and Functional dyspepsia, overlapping symptoms and associated factors in a general population of Bangladesh’ Indian Journal of Gastroenterology, 33, pp. 265–73.
Ford, AC, Forman, D, Bailey, AG, Axon, AT, and Moayyedi, P. (2012) ‘Effect of dyspepsia on survival: a longitudinal 10-year follow-up study’, American Journal of Gastroenterology, 107, pp. 912–21.
Ford, AC, Forman, D, Bailey, AG, Axon, AT, and Moayyedi, P. (2007) ‘Initial poor quality of life and new onset of dyspepsia: results from a longitudinal 10-year follow-up study’, Gut, pp. 321–27.
Talley, NJ, and Ford, AC. (2015) ‘Functional Dyspepsia’, The New England Journal of Medicine, 19, pp.1853- 63.
Chan, WW and Burakoff, R. (2016) ‘Functional (Nonulcer) Dyspepsia’. In: Norton J. Greenberger et al. eds. Current Diagnosis & Treatment Gastroenterology, Hepatology, & Endoscopy. 3rd edition. Boston, Massachusetts: The McGraw-Hill.
Kusters, J, Gerrits, M, Strijp, V, and Vandenbroucke-Grauls, CM. (1997) ‘Coccoid forms of Helicobacter pylori are the morphologic manifestation of cell death’, Infection and Immunity, 65, pp.3672–79.
Miwa, H, Ghoshal, UC, Fock, KM, Gonlachanvit, S, Gwee, KA, Ang, TL, Chang, FY, Hongo, M, Hou, X, Kachintorn, U, Ke, M, Lai, KH, Lee, KJ, Lu, CL, Mahadeva, S, Miura, S, Park H, Rhee, PL, Sugano, K, Vilaichone, RK, Wong, BC, and Bak YT. (2012) ‘Asian consensus report on functional dyspepsia’ Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, 27, pp. 626–41.
Zullo, A, Hassan, C, Francesco, VD, Repici, A, Manta, R, Tomao, S, Annibale, B, and Vaira, D. (2014) ‘Helicobacter pylori and functional dyspepsia: An unsolved issue? World Journal Gastroenterology, 20, pp. 8957-63.
Wong, BC, Lam, SK, Wong, WM, Chen, JS, Zheng, TT, Feng, RE, Lai, KC, Hu, WH, Yuen, ST, Leung, SY, Fong, DY, Ho, J, Ching, CK, Chen, JS, and China Gastric Cancer Study Group. (2004) ‘Helicobacter pylori eradication to prevent gastric cancer in a high-risk region of China: a. randomized controlled trial’, Journal of American Medical Association, 291, pp.187-94.
Rahman, M, Ghoshal, U, Rowshon, A, Ahmed, F, Kibria, M, Hasan, M, Gwee, KA, and Whitehead, W. (2014), ‘Translation and Validation of Enhanced Asian Rome 3 Questionnaires (EAR3-Q) in Bengali Language for Diagnosis of Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders’, American Journal of Gastroenterology, 109, pp.S527– S44.
Sodhi, JS, Javid, G, Zargar, SA, Tufail, S, Shah, A, Khan, BA, Yattoo, GN, Gulzar, GM, Khan, MA, Lone, MI, Saif, RU, Parveen, S, and Shoukat, A. (2013), ‘Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection and the effect of its eradication on symptoms of functional dyspepsia in Kashmir, India’, Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology , 28, PP. 808-13.
Talley, NJ, Janssens, J, Lauritsen, K, Rácz I, Bolling Sternevald, E, and on behalf of the Optimal Regimen Cures Helicobacter Induced Dyspepsia (ORCHID) Study Group. (1999) ‘Eradication of Helicobacter pylori in functional dyspepsia: randomised double blind placebo controlled trial with 12 months' follow up’ British Medical Journal , 318, pp. 833–7.
Du, LI, Chen, BR, Kim, JJ, Kim, S, Shen, JH, and Dai, N. (2016) ‘Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy for functional dyspepsia: Systematic review and meta-analysis’, World Journal of Gastroenterology, 22, pp. 3486- 95.
Ahmed, EU, Alam, R, Alam, F, Ghosh, CK, Dey, SK, Masud, H, Ahmed, DS, Bhuiyan, MMR, Mia, Roy, PK, and Raihan, ASMA. (2009) ‘Comparative study between Metronidazole, Amoxycilin, Omeprazole based therapy and Levofloxacin, Amoxycilin, Omeprazole based therapy for helicobacter pylori eradication in peptic ulcer disease’, Journal of Chittagong Medical College Teachers Association, 20, pp. 29-32.
McColl, K, Murray, L, El-Omar, E, Dickson, A, El-Nujumi, A, Wirz A, Kelman, A, Penny, C, Knill-Jones, R, and Hilditch, T. (1998) ‘Symptomatic benefit from eradicating Helicobacter pylori infection in patients with nonulcer dyspepsia’, 339, pp. 1869-74.