Comparison Between the Efficacies of Amlodipine and Cilnidipine in Treating Hypertensive Patients
Abstract
Background: Controlling systolic blood pressure (SBP) and diastolic blood pressure (DBP) in hypertension (HTN) patients is one of the main challenges. Amlodipine is one of the calcium channel blockers (CCBs) with a remarkable pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic profile. But we have not enough research-based information regarding the effectiveness of amlodipine and cilnidipine in treating hypertension patients. Aim of the study: The objective of this study was to assess the effectiveness of amlodipine and cilnidipine in treating hypertensive patients.
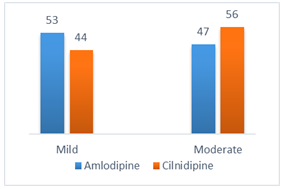
Methods: This study was conducted at the Upazila Health Complex in Shahrasti, Chandpur, Bangladesh, from January 2021 to December 2021. In the study, 200 patients of either sex between the ages of 18 and 60 years were involved. The total number of participants were divided into two equal groups. There were 100 patients in each of the groups. As the part of the hypertension treatment protocol, patients in the first group, received oral amlodipine 5–10 mg/day whereas in other group, patients received oral cilnidipine 10–20 mg/day. During the checkup, the mean systolic and diastolic blood pressure values were noted and evaluated. SPSS 22.0 was used to analyze the data. Results: After 8 weeks of treatment, the cilnidipine group’s SBP gradually decreased from 146.2±12.60 to 130.04±5.023 and its DBP gradually decreased from 94.21±6.86 to 84.34±1.79. On the other hand, in the amlodipine group, a gradual decline of SBP from 151.46±11.21 to 131.62±3.91 and DBP from 95.5±5.80 to 83±2.55 was observed. The results of the paired t-test statistical analysis were statistically significant, where the P value was found as 0.00001. Conclusion: Considering the findings of this current study we can conclude that, both amlodipine and cilnidipine have significant role in controlling blood pressure. But cilnidipine shows some superiority over amlodipine in lowering systolic blood pressure which is equally effective in lowering diastolic blood pressure.
Downloads
References
Pathapati RM, Rajashekar ST, Buchineni M, Meriga RK, Reddy CB, Kumar KP. An open label parallel group study to assess the effects of amlodipine and cilnidipine on pulse wave velocity and augmentation pressures in mild to moderate essential hypertensive patients. J Clin Diagn Res 2015;9:FC13.
Kotchen AT. Hypertensive vascular disease. In: Longo LD, Kasper DL, Hauser SL, Jameson J, Loscalzo J, editor. Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine. 18th ed. New York: Mc Graw Hill; 2012. p. 2042-59.
Sharma LH, Sharma KK. Drug Therapy of Hypertension. In: Principals of Pharmacology. 3rd ed. Hyderabad, New Delhi: Paras Medical Publisher; 2017. p. 262-81.
Walker R, Whittlesea C. Clinical Pharmacy and Therapeutics. 5th ed. London, United Kingdom: Churchill LivingstoneElsevier; London: Arnold Publishers; 2008: 69.
Walker BR, Colledge NR, Ralston SH, Penman ID. Davidson’s Principles and Practice of Medicine. 22nd ed. Edinburgh, United States of America: Churchill Livingstone-Elsevier; 2014.
Cook NR, Cohen J, Hebert PR, Taylor JO, Hennekens CH. Implications of small reductions in diastolic blood pressure for primary prevention. Arch Intern Med 1995;155: 701-9.
Norris K, Neutel JM. Emerging insights in the first-step use of antihypertensive combination therapy. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich) 2007;9 12 Suppl 5:5-14.
Littlejohn TW, Majul CR, Olvera R, Seeber M, Kobe M, Guthrie R, et al. Results of treatment with telmisartanamlodipine in hypertensive patients. J Clin Hypertens 2009;11: 207-13.
Thakurta TG, Panda P. Study of relationship among hypertension, overweight and obesity in individuals of different age groups. Int J Contemp Med Res 2017;4: 733-6.
Chandra SK, Ramesh G. The fourth-generation calcium channel blocker: Cilnidipine. Ind Heart J 2013;65: 691-5.
Osterloh I. The safety of amlodipine. Am Heart J 1989;118: 1114-9.
Adake P, Somashekar HS, Rafeeq PK, Umar D, Basheer B, Baroudi K, et al. Comparison of amlodipine with cilnidipine on antihypertensive efficacy and incidence of pedal edema in mild to moderate hypertensive individuals: A prospective study. J Adv Pharm Technol Res 2015; 6: 81-5.
Ando K, Ueshima K, Tanaka S, Kosugi S, Sato T, Matsuoka H, et al. Comparison of the antialbuminuric effects of L-/N-type and L-type calcium channel blockers in hypertensive patients with diabetes and microalbuminuria: The study of assessment for kidney function by urinary microalbumin in randomized (SAKURA) trial. Int J Med Sci 2013; 10: 1209.
Babu KA. Assessment of efficacy of amlodipine with cilnidipine in hypertensive patients: A comparative study. Int J Contemp Med Res 2017;4: 956-8.
Shanbhag AD, Gowda HN, Laxmegowda. A randomized openlabel study to compare the effects of amlodipine and cilnidipine on heart rate and proteinuria in subjects with hypertension with proteinuria. Natl J Physiol Pharm Pharmacol 2018;8: 1485-90.
Singh J, Singh M, Singh K, Puri A, Kumar K. A Prospective clinical study to determine whether cilnidipine a dual L/Ntype CCB drug therapy can produce resolution of amlodipine induced edema while maintaining adequate control of blood pressure. J Adv Med Dent Sci Res 2018;6: 96-9