Spectrum of neurological disorders in children with neonatal hypoglycemia of western rural Maharashtra.
Abstract
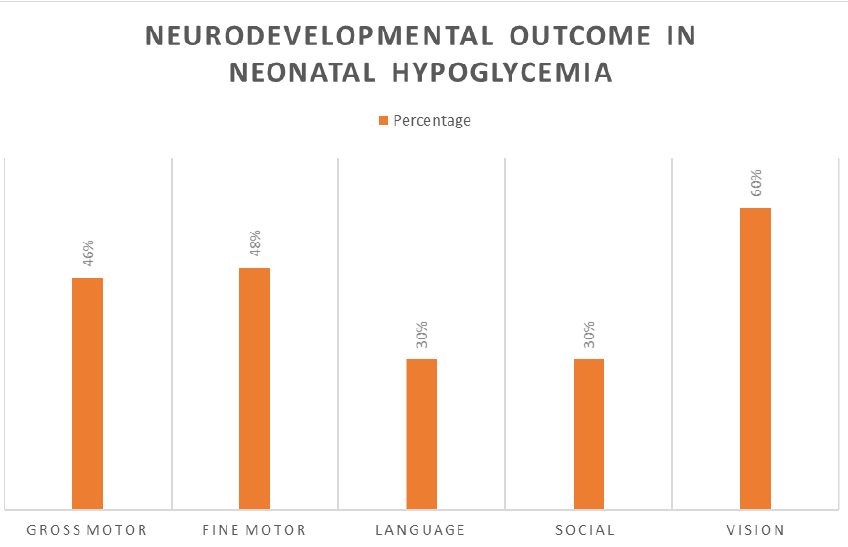
Background: Glucose is an essential metabolic fuel for the brain, and in the newborn the proportionately large brain accounts for almost all of total tissue glucose requirements. Neonatal hypoglycemia is not timely and properly treated, the infants may develop permanent brain injury. Persistent or recurrent hypoglycemia may lead to long-term visual disturbance, hearing impairment, cognitive abnormalities, secondary epilepsy, and other disorders in the central nervous system. Aims and objectives: To study the clinical profile of hypoglycemia in high-risk newborns, as well as neurological squeal. Methods: This is a descriptive cross sectional study was conducted at the department of pediatrics, Dr. Vitthalrao Vikhe Patil Pravara Rural hospital Loni, Maharastra, India, performed on children aged 3 months to 12 years coming to Paediatrics neurology OPD from Feb 2022 to Dec 2023. Results: Out of 60 patients 31(51.6%) presented with seizures. Global developmental delay is found in children, out of which - gross motor delay in 28 (46.67%), fine motor delay in 29(48.33%), social milestone delay in 18(30%) and language mile stone delay in 18(30%) children. 6 (10%)children had autism spectrum disorders. Vision impairment is seen in 36(60%) cases which have significant p value of 0.042. Out of 60 children, 26(43.33%) undergone MRI brain of which in 23(88.46%) of the cases MRI brain was abnormal. Conclusion: Neonatal hypoglycemia is the most common condition in neonatal critical care units, with a significant morbidity rate during infancy and childhood in the form of developmental delay, epilepsy, vision abnormalities, hearing abnormalities and autism etc. It is important to regularly follow these babies for neurodevelopmental assessment to detect and monitor sequalae like developmental delay, epilepsy, visual impairment etc. so as to start early intervention therapy for better neurodevelopmental outcome.
Downloads
References
2. Sunehag AL, Haymond MW. Glucose extremes in newborn infants. Clin Perinatol. (2002) 29:245–60. doi: 10.1016/S0095-5108(02)00006-4 PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
3. Harris D, Weston PJ, Harding JE. Lactate, rather than ketones, may provide alternative cerebral fuel in hypoglycaemic newborns. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. (2015) 100: F161–4. doi: 10.1136/archdischild-2014-3 6435 PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
4. Lou LF, Zhang J. Current Status of Diagnosis and Treatment in Hypoglycemic Encephalopathy. Yi Xue Zong Shu 2010; 16:2008-10. [Google Scholar]
5. Yue SJ, Wang MJ, Wang QH, et al. Congenital hyperinsulinism: a difficult and complicated case study. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi 2006; 8:391-4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
6. Tam EW, Haeusslein LA, Bonifacio SL, et al. Hypoglycemia is Associated with Increased Risk for Brain Injury and Adverse Neurodevelopmental Outcome in Neonates at Risk for Encephalopathy 2012;161:88-93. [PMC free article] [PubMed]
7. Alkalay AL, Sarnat HB, Flores-Sarnat L, et al. Neurologic aspects of neonatal hypoglycemia. Isr Med Assoc J 2005; 7:188-92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
8. Caraballo RH, Sakr D, Mozzi M, et al. Symptomatic occipital lobe epilepsy following neonatal hypoglycemia. Pediatr Neurol 2004; 31:24-29.
9. Yalçın EU, Genç HM, Bayhan A, Anık Y, Kara B. Neurodevelopmental Outcome in Patients with Typical Imaging Features of Injury as a Result of Neonatal Hypoglycemia. Noro Psikiyatr Ars. 2022 Nov 8;59(4):296-302. doi: 10.29399/npa.27997. PMID: 36514522; PMCID: PMC9723839.
10. Edwards T, Alsweiler JM, Gamble GD,
Griffith R, Lin L, McKinlay CJD,
Rogers JA, Thompson B, Wouldes TA,
Harding JE. Neurocognitive Outcomes
at Age 2 Years After Neonatal Hypoglycemia in a Cohort of Participants from the hPOD Randomized Trial. JAMA Netw Open. 2022 Oct 3;5(10): e2235989. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.35989. PMID: 36219444; PMCID: PMC9554702.
11. Gurbuz G, Gur S, Tufekci S, Halis H. A Retrospective Analysis of the Neurological Evaluation of Cases with Neonatal Hypoglycemia. Cureus. 2022 Nov 4;14(11): e31088. doi: 10.7759/cureus.31088. PMID: 36382321; PMCID: PMC9637433.
12. Gu M-H, Amanda F, Yuan T-M. Brain Injury in Neonatal Hypoglycemia: A Hospital-Based Cohort Study. Clinical Medicine Insights: Pediatrics. 2019;13. doi:10.1177/1179556519867953