Clinicoivestigative profile of hypernatremic dehydration in neonates in rural hospital of Maharashtra
Abstract
Aims and objective: To study clinicoinvestigative profile of hypernatremic dehydration of neonates admitted in Dr. B. V. P. Medical College Loni
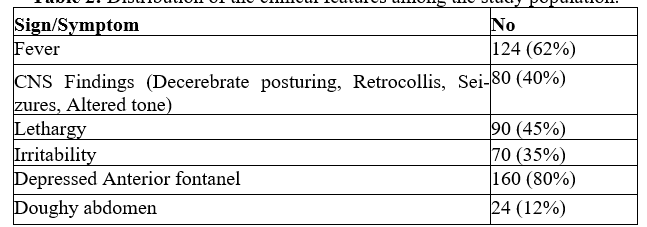
Introduction: Hypernatremic dehydration is a medical emergency which adversely affects central nervous system and kidneys, resulting in high mortality and morbidity, especially in neonates. Neonates are typically affected within the first 2 weeks of life, with those born in hot summers to primigravida mothers with insufficient lactation being particularly prone. Clinical features are usually nonspecific, including weight loss, hyperthermia, irritability, lethargy, hyperbilirubinemia, poor oral intake, oliguria, seizures, and/or shock.
Method: This 18-month study involved 200 neonates admitted to the paediatric department of DR,BVVP Medical College, Loni, with a diagnosis of hypernatremia. It was an observational, descriptive, longitudinal investigation.
Results: The male to female ratio among the 200 patients was 1.2:1. Of the cases, 65% belonged to babies whose mothers were primigravidae, indicating that hypernatremia is more common in these mothers (P<0.0001***). Hypernatremia is more common with LSCS mode of delivery than vaginal birth (P<0.0001***). According to the study, there is a higher incidence during the summer (60%) compared to the monsoon (8%) and winter (32%; p<0.0001***).
Downloads
References
Mujawar NS, Jaiswal AN. Hypernatremia in the neonate: Neonatal hypernatremia and hypernatremic dehydration in neonates receiving exclusive breastfeeding. Indian journal of critical care medicine: peer-reviewed, official publication of Indian Society of Critical Care Medicine. 2017 Jan;21(1):30.
Schwaderer AL, Schwartz GJ. Treating hypernatremic dehydration. Pediatrics in review. 2005 Apr 1;26(4):148-50.
Dieterich CM, Felice JP, O’Sullivan E, Rasmussen KM. Breastfeeding and health outcomes for the mother-infant dyad. Pediatric Clinics. 2013 Feb 1;60(1):31-48.
Caglar MK, Özer I, Altugan FS. Risk factors for excess weight loss and hypernatremia in exclusively breast-fed infants. Brazilian journal of medical and biological research. 2006;39:539-44.
Chumlea WC, Schubert CM, Reo NV, Sun SS, Siervogel RM. Total body water volume for white children and adolescents and anthropometric prediction equations: the Fels Longitudinal Study. Kidney international. 2005 Nov 1;68(5):2317-22.
Sarin A, Thill A, Yaklin CW. Neonatal hypernatremic dehydration. Pediatric annals. 2019 May 1;48(5):e197-200.
Boskabadi H, Akhondian J, Afarideh M, Maamouri G, Bagheri S, Parizadeh SM, Mobarhan MG, Mohammadi S, Frens GA. Long-term neurodevelopmental outcome of neonates with hypernatremic dehydration. Breastfeeding Medicine. 2017 Apr 1;12(3):163-8.
Peñalver Giner, O., Gisbert Mestre, J., Casero Soriano, J., Bernal Ferrer, A., Oltra Benavent, M., & Tomás Vila, M. (2004). Deshidratación hipernatrémica asociada a lactancia materna [Hyper-natremic dehydration associated with breast-feeding]. Anales de pediatria (Barcelona, Spain : 2003), 61(4), 340–343. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1695-4033(04)78399-x
Trotman H, Lord C, Barton M, Antoine M. Hypernatraemic dehydration in Ja-maican breastfed neonates: a 12-year re-view in a baby-friendly hospital. Annals of tropical paediatrics. 2004 Dec 1;24(4):295-300.
Boskabadi H, Godarzi M, Zakerihamidi M, Bagheri F. The study of the relation-ship between hypernatremia in neonates and mode of maternal breast feeding in hospitalized infants in Ghaem Hospital of Mashhad, Iran. The Iranian Journal of Obstetrics, Gynecology and Infertility. 2014 Feb 20;16(90):1-9.
Reilev M, Børch K, Pryds OA. Neonatal hypernatraemic dehydration--why increasing incidence?. Ugeskrift for Laeger. 2007 Mar 1;169(13):1227-31.
Erdemir A, Kahramaner Z, Cosar H, Turkoglu E, Kanik A, Sutcuoglu S, Ozer EA. Comparison of oral and intravenous fluid therapy in newborns with hypernatremic dehydration. The Journal of Maternal-Fetal & Neonatal Medicine. 2014 Mar 1;27(5):491-4.
Farhat AS, Mohamadzadeh A, Mafinejad SH. Evaluation of hypernatremia and related factors among newborns admitted at Emam-Reza hospital.