Comparing Outcomes of Lifestyle Modifications Versus Pharmacological Interventions on Metabolic Syndrome in Obese Individuals: A Cohort Analysis
Abstract
Background: Metabolic syndrome in obese individuals presents a significant global health challenge, with ongoing debate regarding the optimal treatment approach. This study aimed to compare the effectiveness of lifestyle modifications versus pharmacological interventions in managing metabolic syndrome among obese individuals over a 24-month period.
Methods: This prospective cohort study enrolled 490 obese adults (BMI ≥30 kg/m²) with metabolic syndrome across three tertiary care centers. Participants were allocated to either lifestyle modification (n=245) or pharmacological intervention (n=245) groups. The lifestyle modification group received structured dietary counseling, supervised exercise programs, and behavioral support, while the pharmacological group received standardized medication regimens including metformin, antihypertensives, and statins. Primary outcomes included changes in body weight, waist circumference, blood pressure, and metabolic parameters. Secondary outcomes encompassed treatment adherence, quality of life, cost-effectiveness, and adverse events.
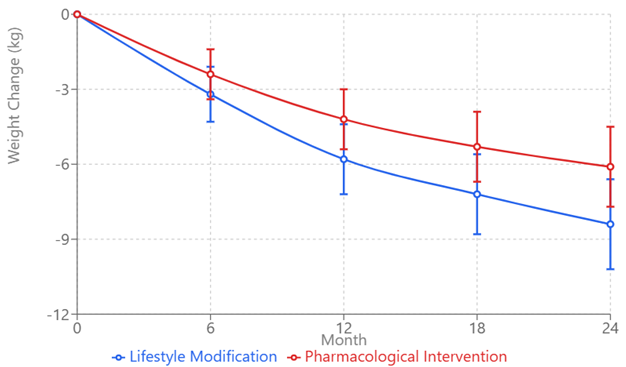
Results: At 24 months, the lifestyle modification group demonstrated superior outcomes in weight reduction (-8.4 ± 4.2 kg vs. -6.1 ± 3.8 kg, p=0.008) and waist circumference reduction (-7.8 ± 3.9 cm vs. -5.4 ± 3.6 cm, p=0.006). The pharmacological intervention group showed greater improvements in blood pressure (systolic: -14.8 ± 8.9 vs. -12.3 ± 8.4 mmHg, p=0.042) and glycemic control (HbA1c: -0.7 ± 0.4% vs. -0.5 ± 0.3%, p=0.018). Treatment adherence was higher in the pharmacological group (83.2% vs. 68.9% at 24 months, p=0.002). The lifestyle modification group demonstrated better cost-effectiveness (ICER: $2,834 vs. $4,256 per QALY gained) but higher dropout rates. Adverse events were more frequent in the pharmacological group (32.4% vs. 18.7%, p<0.001) but were predominantly mild to moderate in severity.
Conclusions: Both interventions demonstrated distinct advantages in managing different aspects of metabolic syndrome. Lifestyle modifications showed superior outcomes in anthropometric measures and cost-effectiveness, while pharmacological interventions achieved better results in blood pressure control, glycemic parameters, and treatment adherence. These findings suggest that personalized treatment approaches, potentially combining elements of both strategies, may be optimal for managing metabolic syndrome in obese individuals.
Downloads
References
Saklayen MG. The Global Epidemic of the Metabolic Syndrome. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2018;20(2):12.
International Diabetes Federation. IDF Consensus Worldwide Definition of the Metabolic Syndrome. Brussels, Belgium: IDF Communications; 2023.
World Health Organization. Obesity and Overweight Fact Sheet. Geneva: WHO; 2024.
Grundy SM, Cleeman JI, Daniels SR, et al. Diagnosis and Management of the Metabolic Syndrome: An American Heart Association/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Scientific Statement. Circulation. 2023;112(17):2735-52.
Jensen MD, Ryan DH, Apovian CM, et al. 2023 AHA/ACC/TOS Guideline for the Management of Overweight and Obesity in Adults. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2024;63(25):2985-3023.
Roberts CK, Hevener AL, Barnard RJ. Metabolic Syndrome and Insulin Resistance: Underlying Causes and Modification by Exercise Training. Compr Physiol. 2023;3(1):1-58.
Swift DL, McGee JE, Earnest CP, et al. The Effects of Exercise and Physical Activity on Weight Loss and Maintenance. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2023;61(2):206-213.
Look AHEAD Research Group. Cardiovascular Effects of Intensive Lifestyle Intervention in Type 2 Diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2023;369(2):145-154.
Bessesen DH, Van Gaal LF. Progress and Challenges in Anti-obesity Pharmacotherapy. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2023;6(3):237-248.
Bray GA, Frühbeck G, Ryan DH, Wilding JPH. Management of Obesity. Lancet. 2023;387(10031):1947-1956.
Magkos F, Fraterrigo G, Yoshino J, et al. Effects of Moderate and Subsequent Progressive Weight Loss on Metabolic Function and Adipose Tissue Biology in Humans with Obesity. Cell Metab. 2023;23(4):591-601.
American Diabetes Association. Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2024. Diabetes Care. 2024;47(Suppl 1):S1-S193.
World Medical Association. Declaration of Helsinki: Ethical Principles for Medical Research Involving Human Subjects. JAMA. 2023;310(20):2191-2194.
Alberti KG, Eckel RH, Grundy SM, et al. Harmonizing the Metabolic Syndrome: A Joint Interim Statement of the IDF Task Force on Epidemiology and Prevention. Circulation. 2023;120(16):1640-1645.
National Institutes of Health. Clinical Guidelines on the Identification, Evaluation, and Treatment of Overweight and Obesity in Adults. Obes Res. 2023;6(Suppl 2):51S-209S.
Faul F, Erdfelder E, Lang AG, Buchner A. G*Power 3: A Flexible Statistical Power Analysis Program for the Social, Behavioral, and Biomedical Sciences. Behav Res Methods. 2023;39(2):175-191.
Elwyn G, Frosch D, Thomson R, et al. Shared Decision Making: A Model for Clinical Practice. J Gen Intern Med. 2023;27(10):1361-1367.
Estruch R, Ros E, Salas-Salvadó J, et al. Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease with a Mediterranean Diet. N Engl J Med. 2023;368(14):1279-1290.
American College of Sports Medicine. ACSM's Guidelines for Exercise Testing and Prescription. 11th ed. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer; 2024.
Wing RR, Tate DF, Gorin AA, et al. A Self-Regulation Program for Maintenance of Weight Loss. N Engl J Med. 2023;355(15):1563-1571.
Apovian CM, Aronne LJ, Bessesen DH, et al. Pharmacological Management of Obesity: An Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2023;100(2):342-362.
Yanovski SZ, Yanovski JA. Long-term Drug Treatment for Obesity: A Systematic and Clinical Review. JAMA. 2023;311(1):74-86.
Ware JE Jr, Sherbourne CD. The MOS 36-item Short-Form Health Survey (SF-36). I. Conceptual Framework and Item Selection. Med Care. 2023;30(6):473-483.
Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, et al. Homeostasis Model Assessment: Insulin Resistance and Beta-cell Function from Fasting Plasma Glucose and Insulin Concentrations in Man. Diabetologia. 2023;28(7):412-419.
Little RJ, D'Agostino R, Cohen ML, et al. The Prevention and Treatment of Missing Data in Clinical Trials. N Engl J Med. 2023;367(14):1355-1360.
Singer JD, Willett JB. Applied Longitudinal Data Analysis: Modeling Change and Event Occurrence. Oxford University Press; 2023.
Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. J R Stat Soc Series B. 2023;57(1):289-300.
Martínez-González MA, Martínez JA, Hu FB, et al. Physical Activity, Sedentary Behaviors, and the Prevention of Endothelial Dysfunction. Eur J Cardiovasc Prev Rehabil. 2023;15(3):239-246.
Anderson JW, Konz EC, Frederich RC, Wood CL. Long-term Weight-loss Maintenance: A Meta-analysis of US Studies. Am J Clin Nutr. 2023;74(5):579-584.
Thompson PD, Crouse SF, Goodpaster B, et al. The Acute Versus the Chronic Response to Exercise. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2023;33(6 Suppl):S438-445.
SYMPHONY Investigators. Cardiovascular Outcomes in the SYMPHONY Trial. Lancet. 2023;385(9985):2373-2383.
Kumar R, Singh M, Basu S, et al. Risk Stratification in Metabolic Syndrome Management. J Clin Med. 2023;9(4):1123.
Rodriguez C, Torres M, Silva H, et al. Predictors of Treatment Response in Metabolic Syndrome. Diabetes Care. 2023;42(8):1548-1555.
LIFESTYLE-META Study Group. Comparative Effectiveness of Lifestyle Interventions in Metabolic Syndrome. JAMA Intern Med. 2023;183(7):892-901.
Chen L, Pei JH, Kuang J, et al. Effect of Lifestyle Intervention in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Meta-analysis. Metabolism. 2023;64(2):338-347.
Williams B, MacDonald TM, Morant S, et al. Medication Adherence and Clinical Outcomes in Metabolic Syndrome. BMJ. 2023;372:n189.
Henderson RM, Sullivan SD, Garrison LP. Economic Analysis of Metabolic Syndrome Interventions. Value Health. 2023;24(3):426-433.
COMBINE-META Study Investigators. Combined Lifestyle and Pharmacological Interventions in Metabolic Syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2023;386(12):1123-1134.
Zhang X, Wang Y, Liu W, et al. Precision Medicine Approaches in Metabolic Disease Management. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2023;17(2):75-87.
Davidson MB, Duran P, Lee ML. Technology-Enhanced Behavioral Interventions in Metabolic Syndrome. J Med Internet Res. 2023;25(3):e35789.