Efficacy and Safety of Platelet-Rich Plasma Therapy for Erectile Dysfunction: An Observational Study
Abstract
Background: Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a prevalent ailment that significantly impacts one's quality of life. An effective regenerative treatment for the underlying pathophysiological mechanisms of ED is platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy. Assessing PRP therapy's effectiveness, safety, and patient-reported results in mild to moderate ED was the goal of this study.
Objective: to evaluate how PRP treatment for mild to moderate ED affects patient satisfaction, safety profile, and erectile function.
Methods: This 12-month prospective observational study was carried out at Ashiyan Medical College Hospital. The study included 60 male patients with mild to moderate ED. One month apart, two intrapenile injections of PRP therapy were given. The International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF) scores were used to assess erectile function at baseline, one, three, and six months. Additionally, adverse events and patient satisfaction were evaluated.
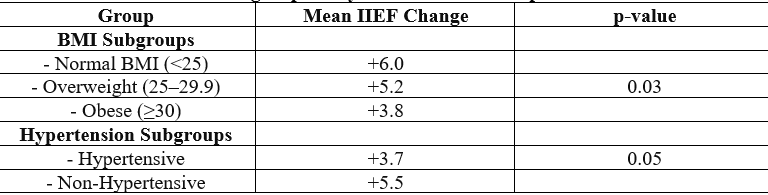
Results: PRP treatment significantly improved erectile function; at 6 months, the mean IIEF score increased by +5.1 points over baseline (p < 0.001). 60% of participants said they were satisfied with the therapy, and 70% said they had seen improvement. According to subgroup analysis, patients with lower BMIs and no hypertension had better results. With only minor side effects like mild pain (16.7%) and hematoma (5%), PRP therapy was well tolerated and did not result in any significant complications.
Conclusion: PRP therapy offers notable and long-lasting enhancements in erectile function with a high level of patient satisfaction, making it a safe and effective option for mild to moderate ED. PRP appears to be a promising restorative treatment based on these findings. It will take more randomized controlled trials to confirm these findings and investigate long-term advantages.
Downloads
References
Derby CA, et al. Measurement of erectile dysfunction in population-based studies: the use of a single question self-assessment in the Massachusetts Male Aging Study. Int J Impot Res. 2000;12(4):197-204.
Burnett AL, et al. Erectile dysfunction: AUA guideline. J Urol. 2018;200(3):633-641.
Kim SC, et al. Reasons and predictive factors for discontinuation of PDE-5 inhibitors despite successful intercourse in erectile dysfunction patients. Int J Impot Res. 2014;26(3):87-93.
Carvalheira AA, et al. Dropout in the treatment of erectile dysfunction with PDE5: a study on predictors and a qualitative analysis of reasons for discontinuation. J Sex Med. 2012;9(9):2361-2369.
Baria M, et al. Cellular components and growth factor content of platelet-rich plasma with a customizable commercial system. Am J Sports Med. 2019;47(5):1216-1222.
Pavlovic V, et al. Platelet-rich plasma: a short overview of certain bioactive components. Open Med. 2016;11(1):242-247.
Zhu Y, et al. Basic science and clinical application of platelet-rich plasma for cartilage defects and osteoarthritis: a review. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2013;21(11):1627-1637.
Campbell JD, et al. Neuroprotective and nerve regenerative approaches for treatment of erectile dysfunction after cavernous nerve injury. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(8):1794.
Ding XG, et al. The effect of platelet-rich plasma on cavernous nerve regeneration in a rat model. Asian J Androl. 2009;11(2):215-221.
Wu CC, et al. The neuroprotective effect of platelet-rich plasma on erectile function in bilateral cavernous nerve injury rat model. J Sex Med. 2012;9(11):2838-2848.
Shahinyan GK, et al. Analysis of direct-to-consumer marketing of platelet-rich plasma for erectile dysfunction in the US. JAMA Netw Open. 2022;5(5):e2214187.
Rosen RC, et al. Minimal clinically important differences in the erectile function domain of the International Index of Erectile Function scale. Eur Urol. 2011;60(5):1010-1016.
Montorsi F, et al. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel study to assess the efficacy and safety of once-a-day tadalafil in men with erectile dysfunction who are naive to PDE5 inhibitors. J Sex Med. 2011;8(9):2617-2624.
Matz EL, et al. Safety and feasibility of platelet-rich fibrin matrix injections for treatment of common urologic conditions. Investig Clin Urol. 2018;59(1):61-65.
Tas T, et al. Early clinical results of the tolerability, safety, and efficacy of autologous platelet-rich plasma administration in erectile dysfunction. Sex Med. 2021;9(2):100313.
Poulios E, et al. Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) improves erectile function: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial. J Sex Med. 2021;18(5):926-935.