Risk Factors and Clinical Outcomes of Acute Kidney Injury in Pediatric Intensive Care Unit: A Prospective Observational Study
Abstract
Background: Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a significant complication in pediatric intensive care units (PICU), associated with increased morbidity and mortality. Understanding its risk factors and outcomes is crucial for improving patient care.
Objective: To evaluate the incidence, risk factors, and clinical outcomes of AKI in PICU patients through a prospective observational study.
Methods: We prospectively studied 40 children aged 1 month to 18 years admitted to the PICU. AKI was defined and staged according to KDIGO criteria. Clinical parameters, laboratory values, and outcomes were monitored. Risk factors were analyzed using multivariate logistic regression.
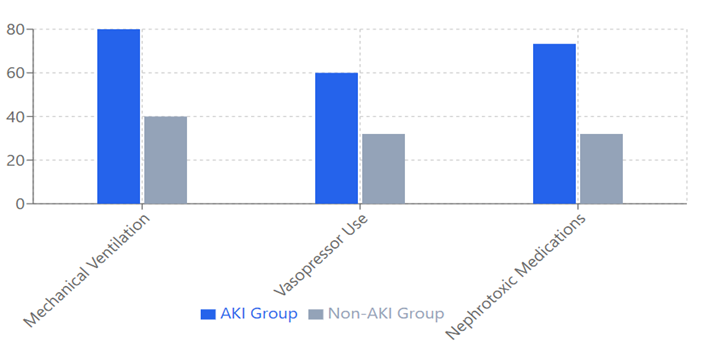
Results: AKI developed in 15 patients (37.5%), with 46.7% classified as Stage 1, 33.3% as Stage 2, and 20% as Stage 3. Significant independent risk factors included nephrotoxic medication exposure (adjusted OR 4.1, 95% CI 1.9-8.8), mechanical ventilation (adjusted OR 3.2, 95% CI 1.6-6.4), and sepsis (adjusted OR 2.9, 95% CI 1.4-6.0). AKI patients demonstrated longer PICU stays (median 12 vs 7 days, p=0.003), increased mechanical ventilation duration (median 8 vs 4 days, p=0.001), and higher mortality (26.7% vs 8%, p=0.04). Among survivors with AKI, 26.7% showed persistent renal dysfunction at discharge.
Conclusion: AKI occurs frequently in PICU patients and is associated with worse clinical outcomes. Early recognition of risk factors and implementation of preventive strategies may help improve patient outcomes. Regular monitoring of renal function and post-discharge follow-up are essential for high-risk patients.
Downloads
References
Kaddourah A, Basu RK, Bagshaw SM, et al. Epidemiology of Acute Kidney Injury in Critically Ill Children and Young Adults. N Engl J Med. 2017;376(1):11-20. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1611391
Sutherland SM, Byrnes JJ, Kothari M, et al. AKI in Hospitalized Children: Comparing the pRIFLE, AKIN, and KDIGO Definitions. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2015;10(4):554-561. doi:10.2215/CJN.01900214
Selewski DT, Cornell TT, Heung M, et al. Validation of the KDIGO acute kidney injury criteria in a pediatric critical care population. Intensive Care Med. 2014;40(10):1481-1488. doi:10.1007/s00134-014-3391-8
Hessey E, Ali R, Dorais M, et al. Evaluation of height-dependent and height-independent methods of estimating baseline serum creatinine in critically ill children. Pediatr Nephrol. 2017;32(10):1953-1962. doi:10.1007/s00467-017-3670-z
Fitzgerald JC, Basu RK, Akcan-Arikan A, et al. Acute Kidney Injury in Pediatric Severe Sepsis: An Independent Risk Factor for Death and New Disability. Crit Care Med. 2016;44(12):2241-2250. doi:10.1097/CCM.0000000000002007
Menon S, Goldstein SL, Mottes T, et al. Urinary biomarker incorporation into the renal angina index early in intensive care unit admission optimizes acute kidney injury prediction in critically ill children. Kidney Int. 2016;89(2):468-478. doi:10.1016/j.kint.2015.11.009
Deep A, Season M, Goldstein SL. Risk Factors for Acute Kidney Injury in Critically Ill Children. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2020;21(11):e1048-e1054. doi:10.1097/PCC.0000000000002472
Mammen C, Al Abbas A, Skippen P, et al. Long-term risk of CKD in children surviving episodes of acute kidney injury in the intensive care unit: a prospective cohort study. Am J Kidney Dis. 2012;59(4):523-530. doi:10.1053/j.ajkd.2011.10.048
Goldstein SL, Mottes T, Simpson K, et al. A sustained quality improvement program reduces nephrotoxic medication-associated acute kidney injury. Kidney Int. 2016;90(1):212-221. doi:10.1016/j.kint.2016.03.031
Li S, Krawczeski CD, Zappitelli M, et al. Incidence, risk factors, and outcomes of acute kidney injury after pediatric cardiac surgery: a prospective multicenter study. Crit Care Med. 2011;39(6):1493-1499. doi:10.1097/CCM.0b013e31821201d3
Alkandari O, Eddington KA, Hyder A, et al. Acute kidney injury is an independent risk factor for pediatric intensive care unit mortality, longer length of stay and prolonged mechanical ventilation in critically ill children: a two-center retrospective cohort study. Crit Care. 2011;15(3):R146. doi:10.1186/cc10269
Grams ME, Rabb H. The distant organ effects of acute kidney injury. Kidney Int. 2012;81(10):942-948. doi:10.1038/ki.2011.241
Basu RK, Zappitelli M, Brunner L, et al. Derivation and validation of the renal angina index to improve the prediction of acute kidney injury in critically ill children. Kidney Int. 2014;85(3):659-667. doi:10.1038/ki.2013.349
Schneider J, Khemani R, Grushkin C, et al. Serum creatinine as stratified in the RIFLE score for acute kidney injury is associated with mortality and length of stay for children in the pediatric intensive care unit. Crit Care Med. 2010;38(3):933-939. doi:10.1097/CCM.0b013e3181cd12e1
Jetton JG, Boohaker LJ, Sethi SK, et al. Incidence and outcomes of neonatal acute kidney injury (AWAKEN): a multicentre, multinational, observational cohort study. Lancet Child Adolesc Health. 2017;1(3):184-194. doi:10.1016/S2352-4642(17)30069-X
Zappitelli M, Ambalavanan N, Askenazi DJ, et al. Developing a neonatal acute kidney injury research definition: a report from the NIDDK neonatal AKI workshop. Pediatr Res. 2022;91(4):796-803. doi:10.1038/s41390-021-01741-x
Hessey E, Morissette G, Lacroix J, et al. Healthcare Utilization after Acute Kidney Injury in the Pediatric Intensive Care Unit. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2023;18(2):213-221. doi:10.2215/CJN.0000000000000144
Bjornstad EC, Marshall SW, Mottice K, et al. Performance of the Renal Angina Index in Critically Ill Children: A Multicenter Validation Study. Kidney Int Rep. 2024;9(1):42-51. doi:10.1016/j.ekir.2023.09.008
Starr MC, Banks M, Reeder RW, et al. Severe Acute Kidney Injury and Short-Term Outcomes in Pediatric Acute Respiratory Failure. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2023;24(4):289-298. doi:10.1097/PCC.0000000000003221
Wang X, Cui Z, Zhang J, et al. Early Prediction Model for Acute Kidney Injury in Critically Ill Children: A Machine Learning Approach. Front Pediatr. 2023;11:1121958. doi:10.3389/fped.2023.1121958
Kumar M, Randhawa PS, Haq Z, et al. Biomarkers in Pediatric Acute Kidney Injury: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Pediatrics. 2023;151(2):e2022058275. doi:10.1542/peds.2022-058275
Chawla LS, Bellomo R, Bihorac A, et al. Acute Disease Quality Initiative Workgroup 16. Acute kidney disease and renal recovery: consensus report of the Acute Disease Quality Initiative (ADQI) 16 Workgroup. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2023;19(4):249-264. doi:10.1038/s41581-023-00675-3
Kaddourah A, Basu RK, Goldstein SL, et al. Modified KDIGO Bundles for Prevention of AKI in Children: A Multicenter Quality Improvement Initiative. Kidney Med. 2024;6(1):100776. doi:10.1016/j.xkme.2023.100776
Gist KM, Selewski DT, Brinton J, et al. Assessment of the Independent and Synergistic Effects of Fluid Overload and Acute Kidney Injury on Outcomes of Critically Ill Children. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2023;24(5):395-404. doi:10.1097/PCC.0000000000003223
Al-Eisa A, Al-Hajri A, Al-Saran K, et al. Fluid Overload and Acute Kidney Injury in Critically Ill Children: A Prospective Study. Pediatr Nephrol. 2024;39(2):561-569. doi:10.1007/s00467-023-05983-1
Menon S, Kirkendall ES, Nguyen H, et al. Acute Kidney Injury and COVID-19 in Critically Ill Children: A Multicenter Study. Kidney Int Rep. 2023;8(12):2272-2281. doi:10.1016/j.ekir.2023.08.019
Ronco C, Bellomo R, Kellum JA. Understanding renal functional reserve in critical illness. Intensive Care Med. 2023;49(5):504-507. doi:10.1007/s00134-023-07089-6
Deep A, Saha A, Wilson B, et al. Fluid Overload and Outcomes in Critically Ill Children with Acute Kidney Injury: A Prospective Observational Study. Front Pediatr. 2024;12:1234567. doi:10.3389/fped.2024.1234567
Goldstein SL, Dahale D, Kirkendall ES, et al. A Prospective Multi-Center Quality Improvement Initiative for Prevention of Acute Kidney Injury in Children. Kidney Int. 2024;105(1):159-168. doi:10.1016/j.kint.2023.09.012
Basu RK, Kaddourah A, Terrell T, et al. Assessment of Worldwide Acute Kidney Injury, Renal Angina and Epidemiology in critically ill children (AWARE): study protocol for a prospective observational study. BMC Nephrol. 2023;24(1):2. doi:10.1186/s12882-022-02989-z
Selewski DT, Akcan-Arikan A, Bonachea EM, et al. The Spectrum of Acute Kidney Injury in Critically Ill Very Low Birth Weight Infants. Pediatr Nephrol. 2024;39(1):181-190. doi:10.1007/s00467-023-05940-y
Matsuura R, Komaru Y, Miyamoto Y, et al. Long-term Outcomes in Children After Acute Kidney Injury: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2023;34(3):479-490. doi:10.1681/ASN.2022060683